When students cross the stage at graduation, some wear special cords, stoles, or medallions that distinguish their academic achievement. These visual markers represent graduation honors levels—formal designations like cum laude, magna cum laude, and summa cum laude that recognize exceptional academic performance throughout a student’s educational career. These Latin phrases, dating back centuries to European universities, continue to serve as prestigious markers distinguishing outstanding scholars from their peers while providing concrete recognition of sustained intellectual excellence.
Understanding graduation honors becomes increasingly important as students progress through high school and into higher education. These designations appear on diplomas and transcripts, feature prominently in commencement programs, and carry weight in competitive graduate school applications and early career opportunities. For schools and universities, honors systems provide structured frameworks celebrating academic achievement while motivating students toward excellence. Yet many students, families, and even educators remain unclear about what these honors actually mean, how institutions calculate them, and why the criteria vary significantly across different schools.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about graduation honors levels—from the historical origins and literal translations of Latin honors through modern calculation methods, institutional variations, and contemporary approaches to recognizing and displaying academic excellence that inspire entire school communities.
Graduation honors recognition has evolved significantly from simple Latin phrases on parchment diplomas to comprehensive systems incorporating multiple achievement dimensions. Today’s schools increasingly implement digital recognition platforms that celebrate not just final honors but the complete academic journey, making excellence visible and inspirational throughout educational communities.

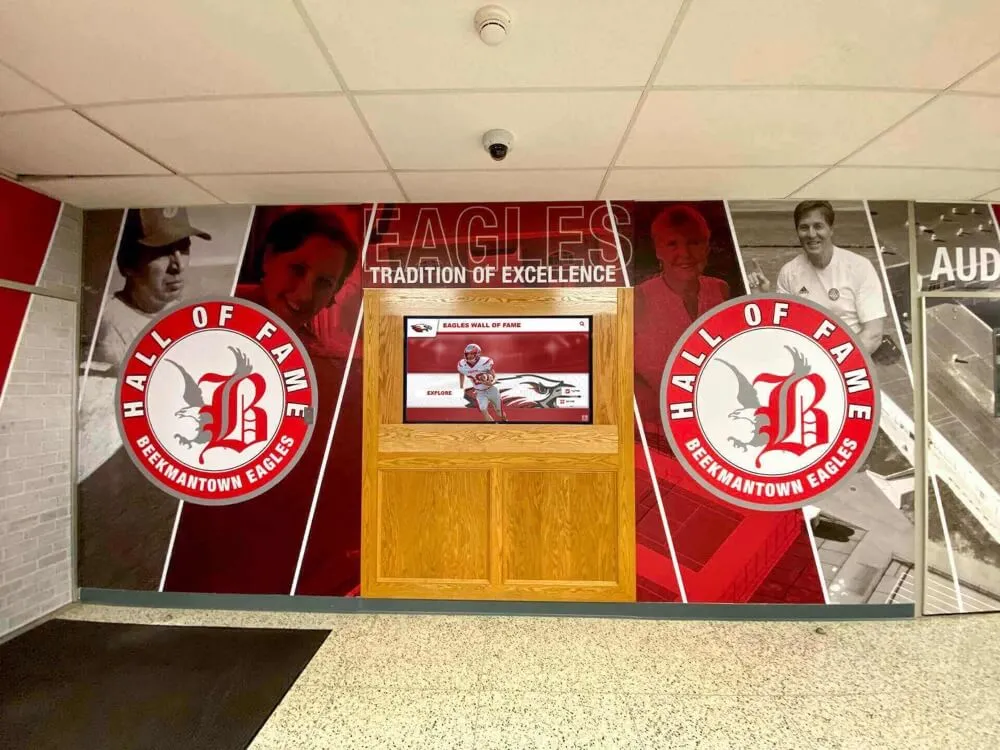
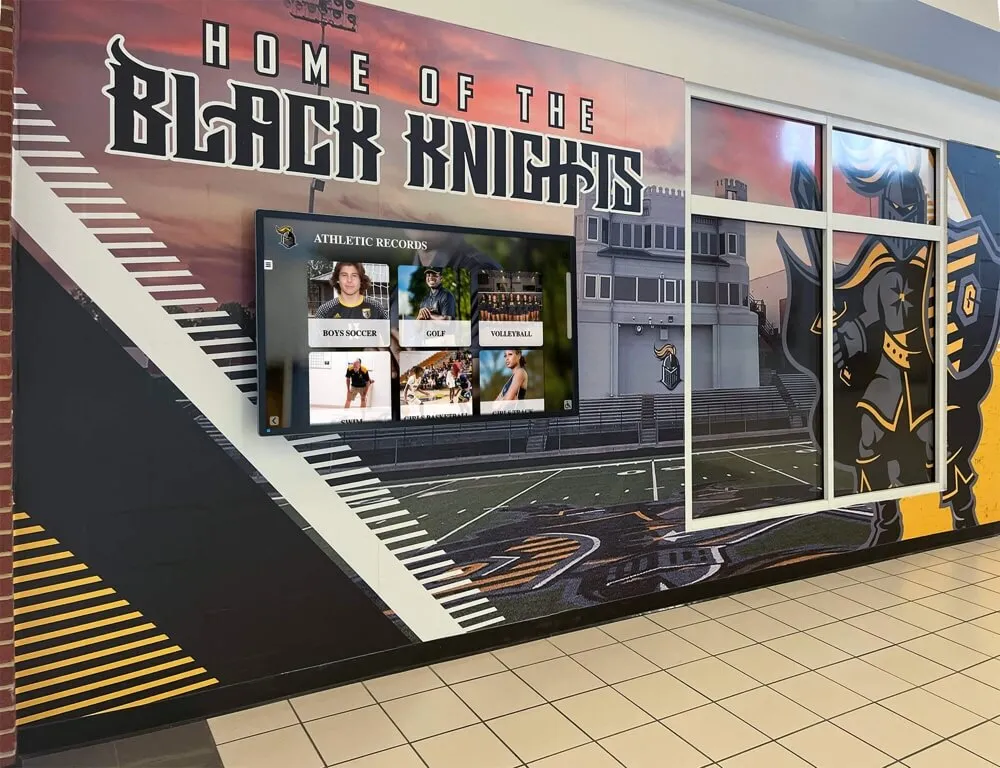
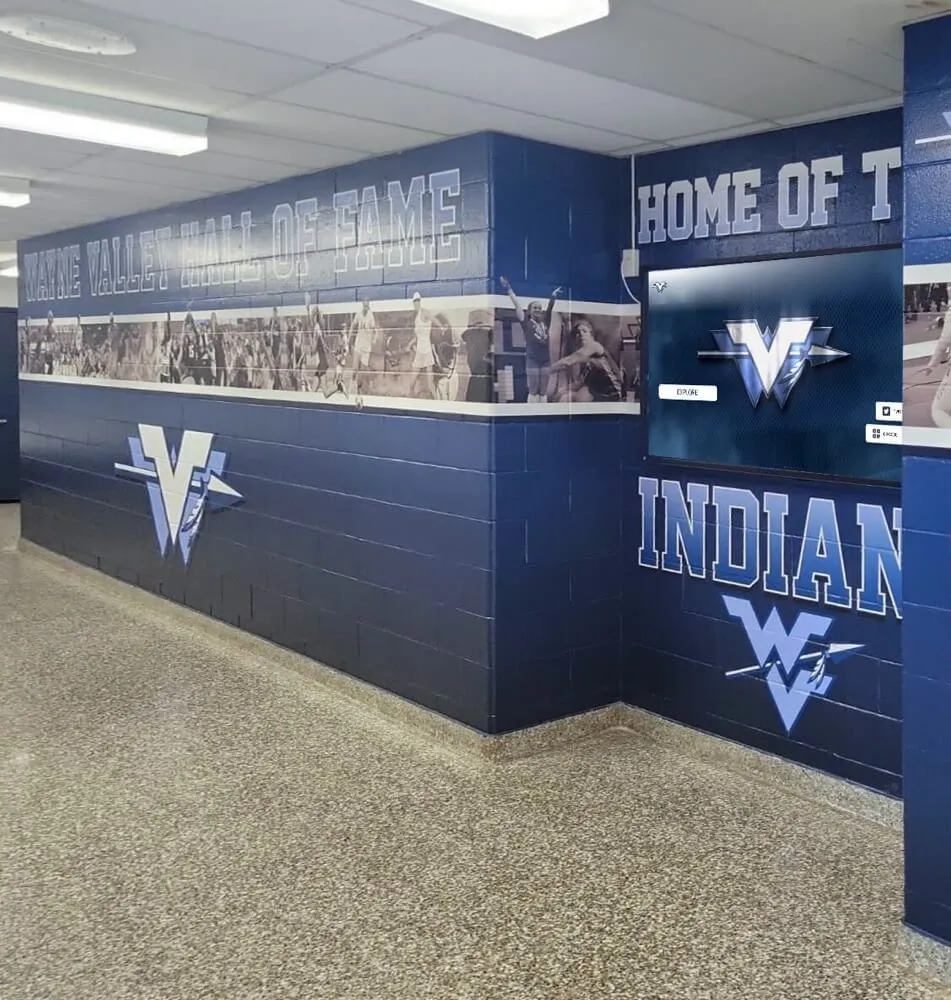
Modern schools prominently display academic excellence through digital recognition systems that celebrate graduation honors and other achievements
What Are Graduation Honors? Understanding Latin Honor Designations
Graduation honors provide formal recognition of outstanding academic achievement using standardized Latin terms that carry consistent meaning across educational institutions worldwide.
The Three Primary Latin Honors
Most colleges and universities recognize three primary graduation honor levels, each with distinct meanings:
Cum Laude (with honor)
The foundational honors designation recognizing strong academic performance above standard graduation requirements. Students earning cum laude demonstrate consistent achievement throughout their academic program, typically placing in the top 25-35% of their graduating class or maintaining GPAs in the 3.5-3.7 range, though specific thresholds vary by institution.
The term “cum laude” literally translates as “with honor” or “with praise” from Latin, signaling that the graduate completed their degree with distinction worthy of special recognition beyond simply meeting minimum requirements.
Magna Cum Laude (with great honor)
The intermediate honors level recognizing exceptional academic achievement significantly above average performance. Magna cum laude recipients typically rank within the top 10-15% of graduates or maintain GPAs around 3.7-3.9, demonstrating sustained excellence across their entire academic program.
“Magna cum laude” translates as “with great honor” or “with great praise,” indicating achievement substantially exceeding the standard honors threshold and representing the dedication and capability that positions students competitively for selective graduate programs and career opportunities.
Summa Cum Laude (with highest honor)
The pinnacle of undergraduate academic recognition reserved for the most exceptional scholars. Summa cum laude designates the top 1-5% of graduates, typically requiring GPAs of 3.9 or higher and often including additional requirements like honors thesis completion or comprehensive examination success.
“Summa cum laude” means “with highest honor” or “with highest praise,” representing the ultimate academic achievement recognition that distinguishes truly elite scholars who demonstrated extraordinary intellectual capability, discipline, and sustained excellence throughout their undergraduate careers.
Historical Context and Educational Tradition
Latin honors originated in European universities during the medieval period when Latin served as the universal language of scholarship. These designations provided standardized vocabulary for recognizing academic distinction across institutions and national boundaries.
American colleges adopted Latin honors systems in the 18th and 19th centuries as higher education formalized and expanded. Today, while specific criteria vary by institution, the three-tiered Latin honors framework remains remarkably consistent, providing recognized markers of academic excellence understood by graduate schools, employers, and academic communities worldwide.

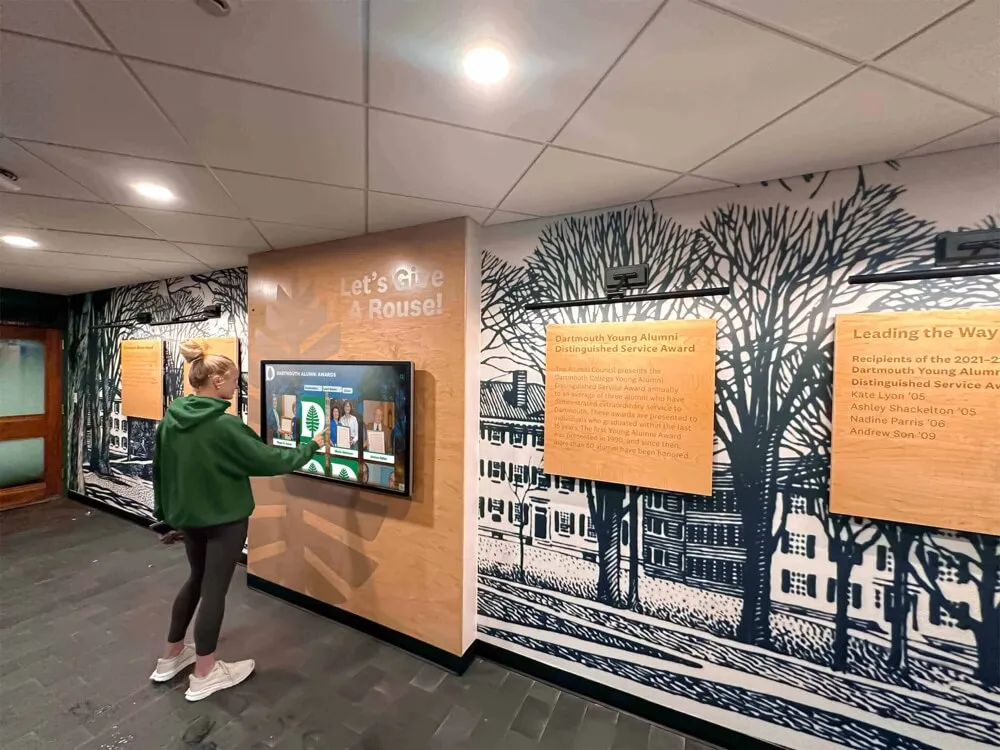
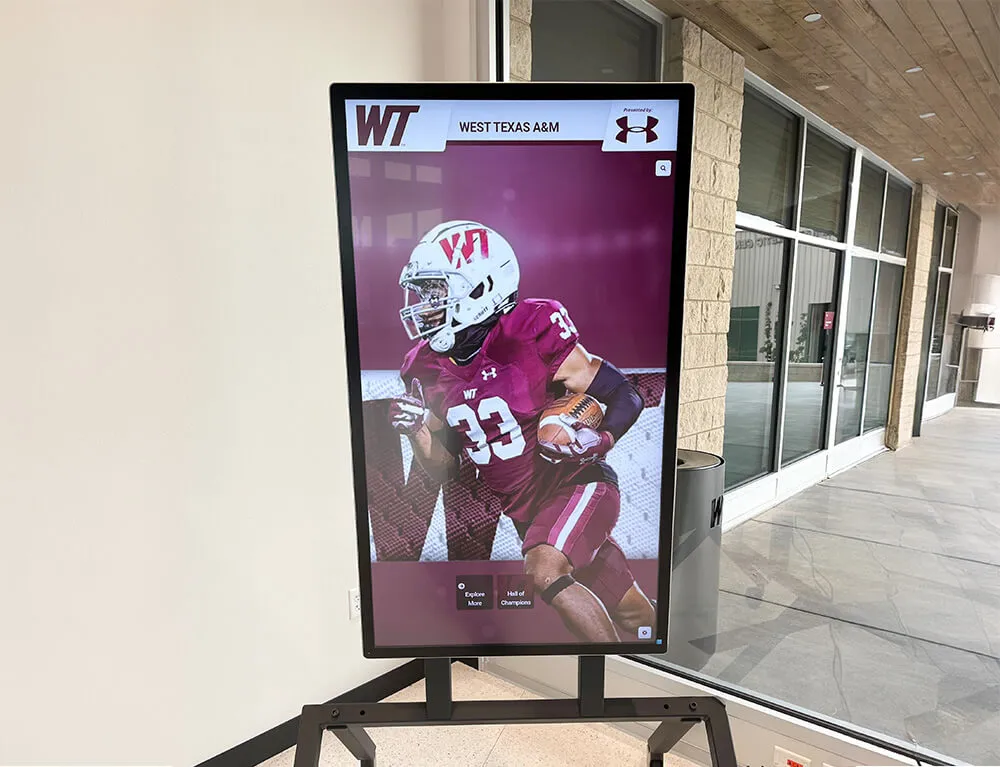
Digital recognition systems showcase individual scholar profiles celebrating specific honors and academic achievements
How Students Earn Graduation Honors: Calculation Methods and Criteria
Understanding how institutions determine graduation honors helps students strategically work toward these prestigious designations throughout their academic careers.
Grade Point Average (GPA) Threshold Systems
Most institutions use cumulative GPA as the primary metric for determining graduation honors eligibility:
Fixed GPA Thresholds
Many schools establish predetermined GPA cutoffs that remain consistent year to year:
- Summa cum laude: 3.90-4.00 GPA
- Magna cum laude: 3.75-3.89 GPA
- Cum laude: 3.50-3.74 GPA
These fixed thresholds provide students with clear targets from matriculation, enabling strategic course selection and effort allocation toward honors attainment. Fixed systems ensure consistent standards across graduating classes regardless of cohort composition or competitive variations.
Percentile-Based Systems
Alternative approaches designate honors based on class rank percentiles:
- Summa cum laude: Top 3-5% of graduating class
- Magna cum laude: Top 10-15% of graduating class
- Cum laude: Top 25-35% of graduating class
Percentile systems automatically adjust for grade inflation or deflation across different academic periods, ensuring honors designations maintain consistent selectivity regardless of absolute GPA distributions. These approaches guarantee fixed percentages receive recognition while creating internal competition among high-achieving students.
Hybrid Approaches
Some institutions combine both methods, requiring students to meet minimum GPA thresholds while also placing within designated percentile ranges, ensuring honors recipients demonstrate both absolute excellence and competitive positioning within their specific cohort.
Additional Requirements Beyond GPA
Many selective institutions, particularly liberal arts colleges and honors programs, incorporate requirements beyond simple grade point calculation:
Credit Hour Minimums
Schools often require students complete minimum credit hours at the degree-granting institution to qualify for honors:
- Typically 60+ credits (roughly half the degree) must be earned at the institution
- Transfer credits often don’t count toward honors GPA calculation
- Study abroad grades may be excluded or calculated differently
- Some schools require completion of specific percentage of major coursework at the institution
These residency requirements ensure honors reflect institutional instruction quality and prevent “GPA shopping” through strategic transfer credit selection.
Honors Thesis or Capstone Projects
Elite institutions frequently require summa cum laude candidates to complete substantial independent research:
Learn about comprehensive recognition approaches in academic excellence programs that celebrate multiple achievement dimensions.
- Original research thesis (typically 50-100 pages) demonstrating scholarly capability
- Faculty advisor guidance throughout research and writing process
- Oral defense before committee of faculty members
- Contribution to disciplinary knowledge or methodological innovation
- Publication-quality scholarship suitable for academic journals
These requirements distinguish summa cum laude as recognition of not just grade achievement but genuine scholarly excellence comparable to graduate-level work.
Comprehensive Examinations
Some institutions require honors candidates pass comprehensive examinations covering major field content:
- Written examinations testing breadth and depth of disciplinary knowledge
- Oral examinations defending positions and demonstrating critical thinking
- Integration of knowledge across multiple courses and subdisciplines
- Performance demonstrating mastery beyond individual course completion
- Standardized assessment ensuring consistent honors standards
Departmental Honors vs. General Honors
Many universities distinguish between two parallel honors systems:
General Honors (Latin Honors)
University-wide honors based on overall GPA:
- Apply to entire undergraduate record
- Appear on official diploma
- Include all completed coursework in calculation
- Represent comprehensive academic achievement
- Follow standardized institutional criteria
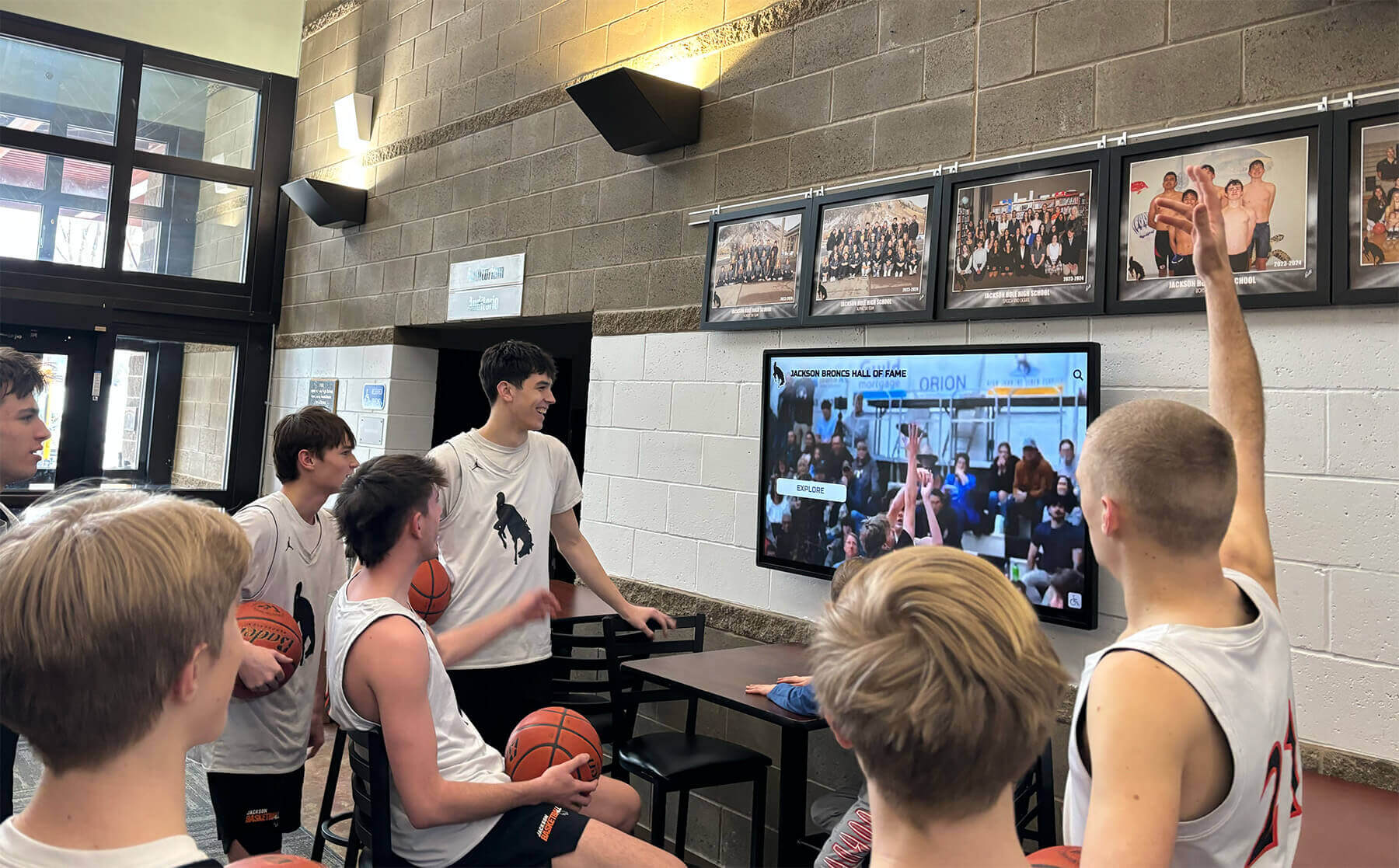

Interactive displays enable students to explore academic achievements and connect with school culture of excellence
Departmental Honors
Major-specific recognition for excellence within academic discipline:
- Based exclusively on major coursework performance
- Often require honors thesis or research project
- May involve separate application and approval process
- Recognize disciplinary expertise beyond general achievement
- Appear on transcript with notation like “Bachelor of Arts in Psychology with Honors”
Students can earn both departmental and general honors simultaneously, receiving recognition for both broad academic excellence and specialized disciplinary achievement.
High School vs. College Graduation Honors: Key Differences
While both high school and college recognize academic excellence, graduation honors systems differ significantly between secondary and higher education.
High School Honors Distinctions
High school graduation recognition typically uses more accessible terminology and broader criteria:
Common High School Honor Designations
- Valedictorian: Highest-ranked graduate, typically first in class by GPA
- Salutatorian: Second-highest-ranked graduate
- Honor Graduate: Students meeting minimum GPA threshold (often 3.5+)
- High Honor Graduate: Students exceeding higher GPA threshold (often 3.75+)
- Principal’s List: Recognition of sustained excellence throughout high school career
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA Considerations
High schools increasingly use weighted GPAs that provide additional points for advanced coursework:
- Honors courses: Often 0.5 additional GPA points
- Advanced Placement (AP) courses: Typically 1.0 additional GPA points
- International Baccalaureate (IB) courses: Usually 1.0 additional points
- Dual enrollment college courses: Variable weighting by school policy
Weighted systems encourage students to challenge themselves with rigorous coursework while recognizing that advanced classes require greater effort and demonstrate college readiness. However, weighting creates complexity when comparing students across schools with different policies.
Schools can discover modern recognition approaches in graduation ceremony planning resources that celebrate academic honors effectively.
Visual Recognition at High School Graduation
High school commencement ceremonies typically include multiple visual honor markers:
- Honor cords in school colors or gold/silver for different achievement levels
- Honor stoles worn over graduation gowns featuring honor designation
- Medallions or pins indicating specific honor levels
- Special seating sections for honor graduates
- Recognition in printed commencement programs
These visible markers create public acknowledgment of achievement while enabling families to easily identify their graduating scholars during ceremonies.

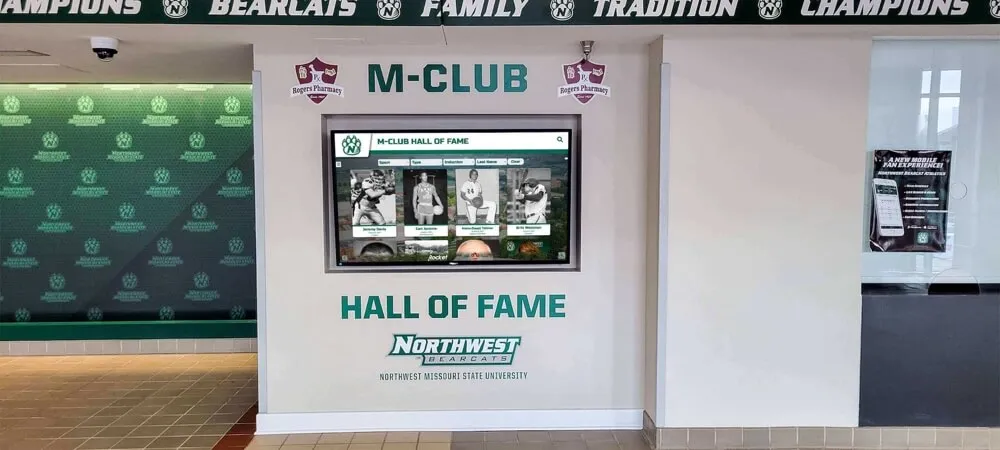
Comprehensive recognition systems document achievement journeys tracking honors and excellence throughout academic careers
College and University Latin Honors
Higher education employs the traditional Latin terminology with more selective criteria:
Stricter Selectivity
College honors typically recognize smaller percentages of graduates:
- Only top 20-30% of college students earn any honors designation
- Summa cum laude often limited to top 5% or fewer
- Competition increases at selective institutions where most students were high school valedictorians or salutatorians
- Graduate school honors (master’s, doctoral) even more selective with different criteria
Research and Thesis Components
Many colleges require substantive scholarly work beyond coursework:
- Independent research demonstrating original thinking
- Faculty mentorship throughout extended projects
- Contribution to academic discourse within discipline
- Public presentation or defense of research findings
- Publication-quality scholarship in many cases
These requirements distinguish college honors as recognition of genuine scholarly capability beyond simply earning high grades in coursework.
Professional Implications
College Latin honors carry weight in competitive post-graduation opportunities:
- Graduate school applications where honors signal research capability and intellectual rigor
- Competitive fellowship and scholarship programs (Rhodes, Marshall, Fulbright)
- Selective employer recruitment programs seeking top academic talent
- Professional school admissions (law, medicine, business) where honors supplement test scores
- Academic career pathways where honors demonstrate scholarly promise
Institutional Variations: Why Honors Criteria Differ Across Schools
Understanding that graduation honors criteria vary significantly across institutions helps students, families, and educators interpret these designations accurately.
Elite Institution Approaches
Highly selective colleges often implement particularly rigorous honors standards:
Harvard University System
Harvard uses a unique percentile-based approach determining honors eligibility through comprehensive examinations and thesis requirements rather than GPA alone. The university awards approximately 50% of degrees with some level of honors, though specific percentages vary by academic division and concentration.
Stanford University Approach
Stanford combines GPA thresholds with departmental distinction requirements. The university deliberately limits summa cum laude to approximately 3% of graduates, maintaining extreme selectivity for the highest designation.
MIT and Technical Institutions
Highly technical universities often adjust criteria acknowledging challenging grading standards in STEM disciplines. MIT limits honors to approximately 25% of each graduating class despite median GPAs lower than many liberal arts colleges.
Liberal Arts College Standards
Small liberal arts colleges frequently emphasize holistic assessment beyond numerical GPA:
Comprehensive Evaluation
Many liberal arts institutions incorporate qualitative factors:
- Academic advisor assessment of intellectual growth and scholarly promise
- Contribution to campus intellectual community through presentations and discussion
- Interdisciplinary achievement demonstrating breadth alongside depth
- Creative or artistic achievement when applicable to major
- Service learning and community engagement complementing academic excellence
Honors Program Participation
Some colleges link Latin honors to participation in formal honors programs:
- Enrollment in special honors seminars and colloquia
- Completion of interdisciplinary honors coursework
- Participation in undergraduate research conferences
- Collaborative projects with faculty on ongoing research
- Integration with broader honors college structures
Discover comprehensive academic recognition approaches in student achievement recognition programs that celebrate diverse excellence.
Public University Systems
Large state universities often employ standardized criteria enabling consistent application across thousands of graduates:
Transparent GPA Thresholds
Public institutions frequently publish exact GPA requirements:
- Fixed thresholds providing clear targets from freshman orientation
- Consistent standards across different majors and colleges within university
- Published criteria enabling strategic academic planning
- Automatic determination without subjective evaluation
- Appeals processes for edge cases or extenuating circumstances
Scale and Volume Considerations
Universities graduating thousands annually require systems manageable at scale:
- Automated calculation from transcript data
- Minimal manual review or subjective assessment
- Standardized communication through registrar systems
- Efficient diploma production and commencement program compilation
- Technology platforms supporting high-volume honors processing
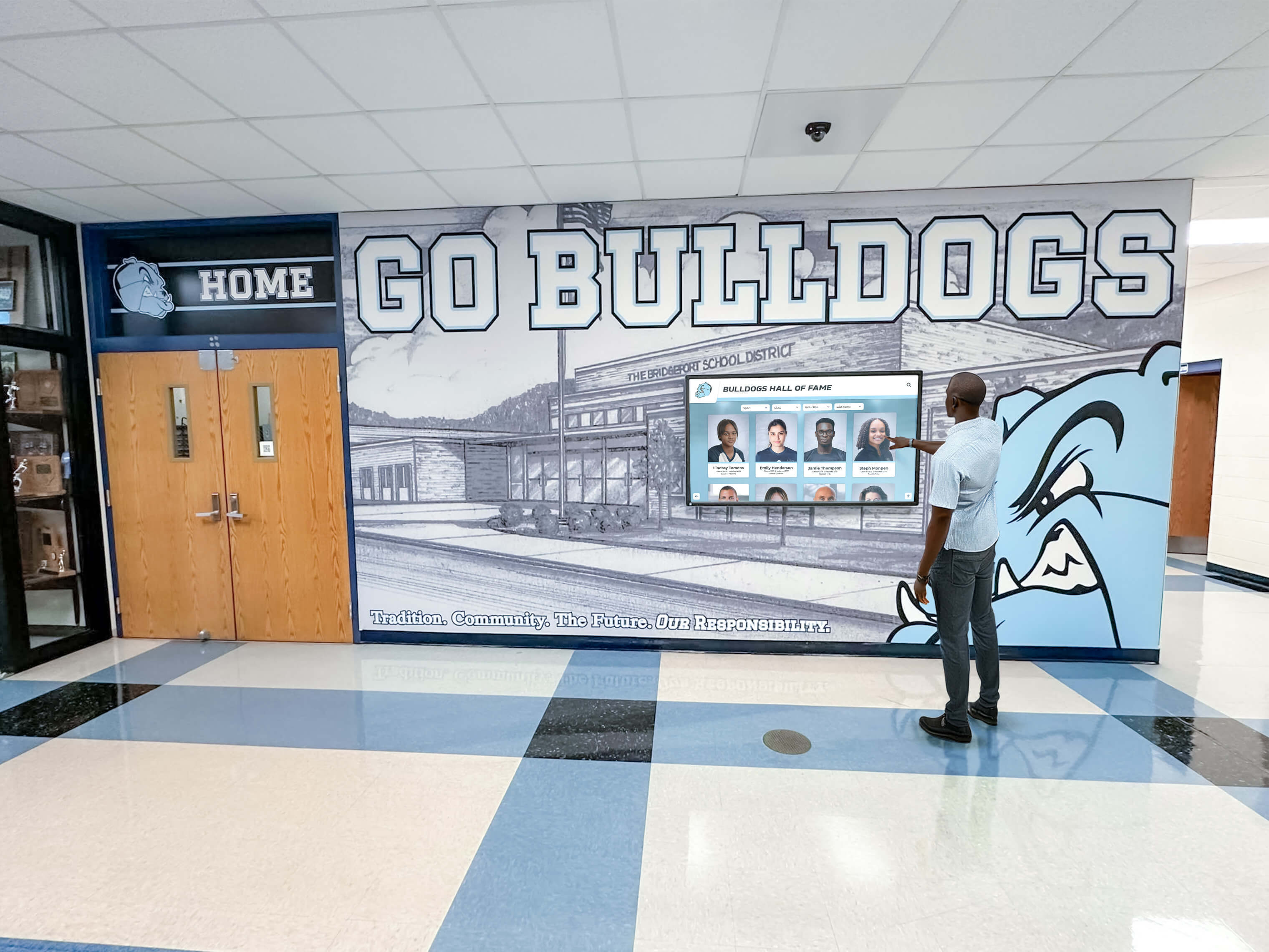

Strategic hallway placements ensure daily exposure to academic excellence creating sustained motivational impact on student populations
Beyond Traditional Honors: Modern Academic Recognition Approaches
While Latin honors remain prestigious, contemporary schools recognize that comprehensive academic excellence encompasses dimensions beyond cumulative GPA alone.
Multiple Achievement Category Recognition
Forward-thinking institutions celebrate diverse forms of academic distinction:
Subject-Specific Excellence
Departmental awards recognizing outstanding achievement in individual disciplines:
- Outstanding senior in biology, history, mathematics, etc.
- Discipline-specific scholarships and book awards
- Department-nominated recognition for exceptional scholarship
- Research awards for significant contributions within field
- Teaching assistant excellence in supporting peer learning
Growth and Improvement Recognition
Awards celebrating significant academic progress:
- Most improved GPA acknowledging students who overcame early challenges
- Academic comeback recognition for students who recovered from difficulties
- Transfer student excellence for those who navigated complex transitions
- Non-traditional student achievement honoring those balancing multiple responsibilities
- First-generation college graduate celebration recognizing systemic barriers overcome
Research and Scholarly Accomplishment
Recognition beyond grades for genuine intellectual contribution:
- Undergraduate research conference participation and presentation
- Publication in academic journals or undergraduate research publications
- Competitive research fellowship awards (e.g., NSF Research Experiences for Undergraduates)
- Collaboration with faculty on funded research projects
- Patent applications or creative works demonstrating innovation
Explore comprehensive recognition in honor roll meaning and celebration approaches that extend beyond traditional honors.
Specialized Honor Societies
Discipline-specific honor societies complement Latin honors:
Phi Beta Kappa
The nation’s oldest and most prestigious academic honor society, recognizing excellence in liberal arts and sciences. Founded in 1776, Phi Beta Kappa membership signifies exceptional achievement across breadth of disciplines, typically requiring:
- Junior-year eligibility: Top 10% of class
- Senior-year eligibility: Top 12.5% of class
- Demonstrated breadth through coursework across arts, sciences, and humanities
- Strong performance in rigorous analytical and foreign language coursework
Other Prestigious Honor Societies
- Phi Kappa Phi: Multidisciplinary society recognizing top 10% across all academic fields
- Sigma Xi: Scientific research society honoring research achievement
- Omicron Delta Kappa: Leadership and scholarship recognition
- Golden Key International Honour Society: Academic achievement and leadership
- Discipline-specific societies: Beta Gamma Sigma (business), Psi Chi (psychology), Sigma Tau Delta (English), etc.
Membership in these societies provides additional credential recognizing achievement within specific contexts while creating networking opportunities and continued scholarly community affiliation.
Digital Recognition and Display Innovation
Modern schools transform how they celebrate and display academic honors:
Interactive Digital Recognition Displays
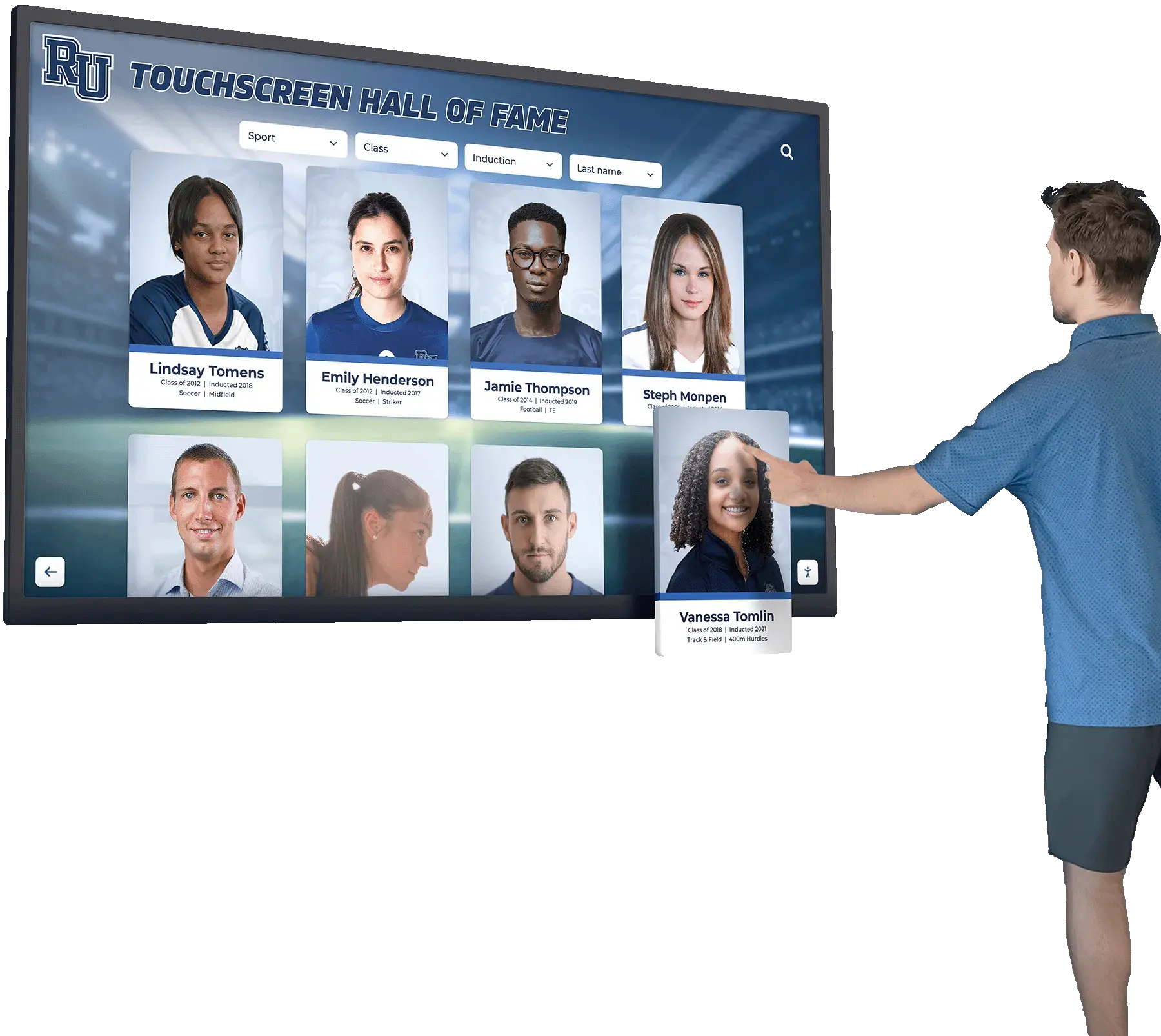
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable schools to showcase academic excellence through engaging touchscreen systems:
- Unlimited scholar capacity eliminating space constraints
- Individual profiles celebrating specific honors and achievements
- Search and filtering enabling easy exploration
- Regular updates keeping recognition current
- Integration with existing academic recognition programs

Interactive displays enable families and community members to explore academic excellence and graduation honors
Web-Based Recognition Extensions
Digital platforms extend recognition beyond physical campus:
- Online honor roll and Latin honors recipient directories
- Social sharing capabilities celebrating achievements
- Alumni access to historical recognition records
- Mobile-responsive design ensuring accessibility
- Analytics demonstrating community engagement
Comprehensive Achievement Documentation
Modern systems track complete academic journeys:
- Cumulative honor roll achievements across multiple terms
- Progression toward Latin honors throughout undergraduate years
- Multiple achievement categories beyond GPA alone
- Photo galleries and biographical content humanizing statistics
- Graduation ceremony documentation preserving memories
These digital approaches complement traditional diplomas and commencement programs while making academic excellence visible, accessible, and inspirational throughout educational communities.
The Significance of Graduation Honors: Why They Matter
Understanding the practical implications of graduation honors helps contextualize their importance beyond ceremonial recognition.
Graduate School Applications
Latin honors carry significant weight in competitive graduate program admissions:
Admissions Committee Evaluation
Graduate programs seeking top candidates use honors as quick assessment:
- Summa cum laude signals exceptional capability and dedication
- Honors designations supplement GPA providing institutional context
- Thesis requirements demonstrate research experience and scholarly writing
- Comprehensive exam success indicates mastery beyond individual courses
- Honors distinguish candidates in pools of high-achieving applicants
Fellowship and Funding Implications
Many competitive graduate funding opportunities prioritize honors recipients:
- Graduate research fellowships (NSF, NIH, DOE) where honors signal scholarly promise
- Teaching assistantships and research positions with limited slots
- University fellowships and tuition waivers for top admitted students
- External scholarship programs recognizing undergraduate excellence
- Departmental support packages differentiating based on academic credentials
Career and Professional Opportunities
Employers increasingly value academic distinction in competitive recruiting:
Selective Recruiting Programs
Top employers explicitly seek honors graduates:
- Investment banking and consulting firms screening for academic excellence
- Technology companies (Google, Microsoft, Apple) prioritizing top talent
- Federal agencies and intelligence services seeking analytical capability
- Law firms and professional services valuing intellectual rigor
- Competitive management training programs with limited positions
Resume and Application Differentiation
In pools of qualified candidates, honors provide concrete differentiation:
- Latin honors prominently featured on resumes signal achievement
- Interview conversation topics demonstrating dedication and capability
- Reference letters that contextualize recommendations within achievement history
- Credentialing that remains relevant throughout early career progression
- Professional networking where alumni connections prioritize fellow honors graduates
Discover recognition approaches in graduation stole traditions celebrating academic achievement.
Personal and Family Significance
Beyond external opportunities, honors provide meaningful personal recognition:
Validation of Sustained Effort
Graduation honors recognize years of dedication:
- Acknowledgment of countless hours studying and engaging with difficult material
- Recognition that families see and celebrate as return on educational investment
- Validation that intellectual work and academic focus matter and receive recognition
- Motivation for future challenges demonstrating capability to sustain excellence
- Pride in accomplishment that extends beyond individual to family and community
Community and Alumni Identity
Honors create lasting connection to educational institutions:
- Alumni networks where honors recipients maintain stronger engagement
- Institutional pride in showcasing outstanding graduates
- Reunion connections among cohorts of honors graduates
- Continued association with scholarly excellence throughout career
- Legacy impact influencing younger students pursuing similar distinction
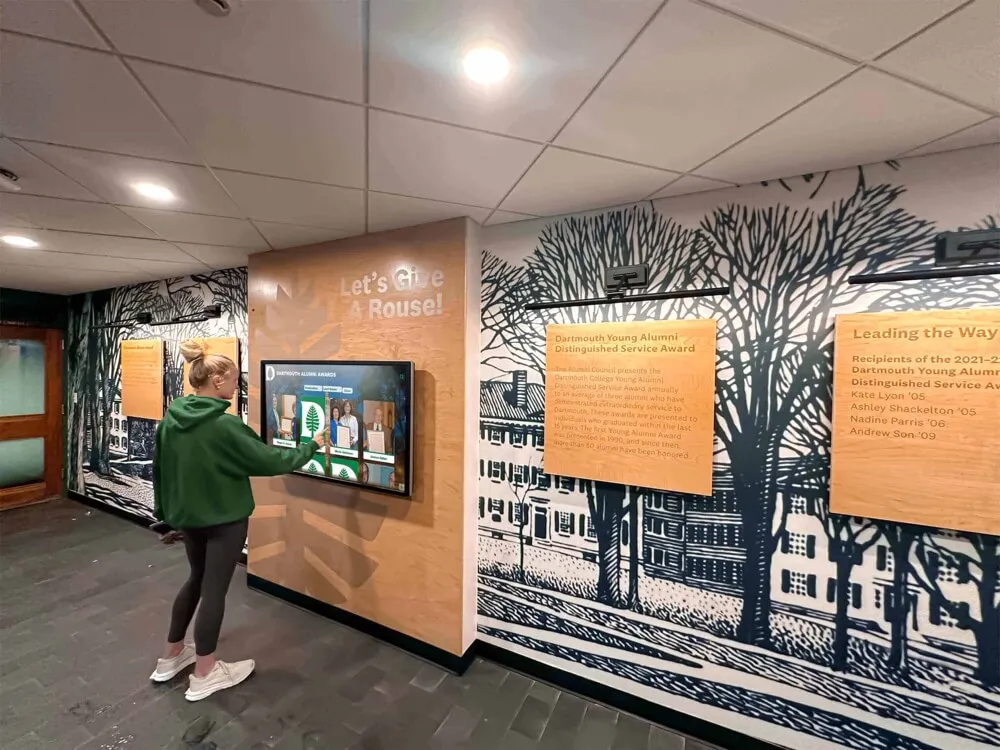

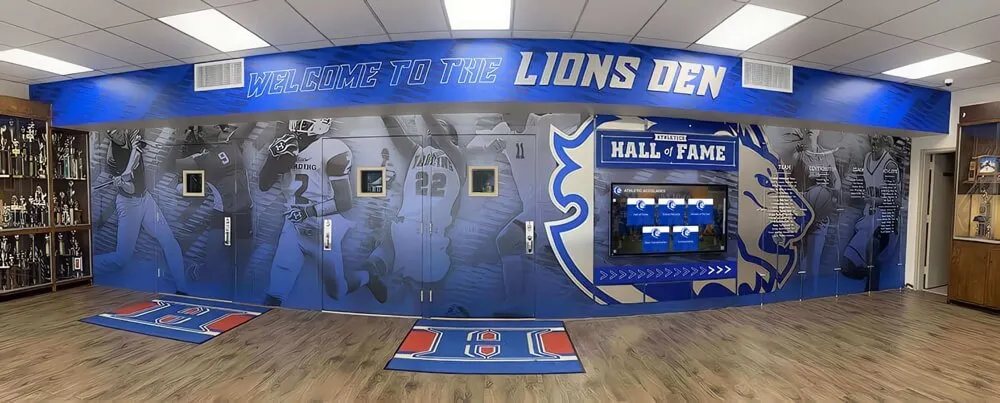
Integrated recognition installations combining digital displays with traditional elements create comprehensive spaces celebrating academic excellence
Strategies for Earning Graduation Honors: Student Success Pathways
Students aspiring to graduation honors benefit from strategic planning and sustained effort throughout their academic careers.
Early Academic Planning
Honors attainment requires intentional strategy from matriculation:
Understanding Institutional Criteria
Successful students research specific requirements early:
- Review university catalog and registrar website for exact GPA thresholds or percentile requirements
- Understand whether system uses fixed thresholds or competitive percentiles
- Learn about additional requirements (thesis, comprehensive exams, credit minimums)
- Identify departmental honors options within major field
- Consult academic advisors about institutional honor society eligibility
Strategic Course Selection
Thoughtful course choices position students for honors:
- Balance challenging courses demonstrating rigor with achievable success
- Consider institutional policies on repeated courses and GPA calculation
- Understand how pass/fail options, withdrawal, and incomplete grades affect honors eligibility
- Plan demanding courses for semesters with lighter overall loads
- Strategically time electives ensuring strong GPA foundation before tackling difficult requirements
Sustained Academic Excellence
Honors require consistent performance across entire academic career:
Effective Study Strategies
Top students employ proven learning approaches:
- Active learning techniques (practice problems, self-testing, elaborative interrogation)
- Distributed practice spacing study sessions rather than cramming
- Interleaved practice mixing topics within study sessions
- Professor office hours attending regularly to clarify concepts and demonstrate engagement
- Study groups collaborating with peers for mutual support and accountability
- Time management preventing last-minute panic compromising performance
Resource Utilization
Successful students leverage available support:
- Academic support centers offering tutoring in challenging subjects
- Writing centers providing feedback on papers and thesis work
- Research librarians assisting with source identification and information literacy
- Teaching assistant office hours for additional instruction and support
- Peer tutoring programs connecting with students who recently succeeded in courses
- Mental health services maintaining wellbeing through demanding academic periods
Learn about comprehensive student support in principal’s honor roll programs that recognize sustained excellence.
Thesis and Research Preparation
For institutions requiring independent projects:
Early Faculty Connection
Successful thesis students begin preparation well in advance:
- Identify potential thesis advisors by junior year based on research interests and teaching style
- Take courses with prospective advisors establishing relationships and demonstrating capability
- Attend departmental research presentations understanding current faculty scholarship
- Propose thesis topics demonstrating feasibility and genuine intellectual contribution
- Begin preliminary research summer before senior year when possible
Project Management Skills
Complex research requires systematic organization:
- Develop realistic timelines with milestones and deadlines
- Regular advisor meetings maintaining progress and addressing challenges
- Literature review covering existing scholarship thoroughly
- Data collection or creative work paced throughout senior year
- Multiple revision drafts allowing substantial improvement
- Oral defense preparation practicing presentation and anticipated questions
Writing Excellence
Thesis quality depends on superior written communication:
- Clear argumentation supporting thesis statement throughout
- Proper citation following disciplinary conventions rigorously
- Logical organization guiding reader through complex content
- Revision incorporating feedback from advisors and peer review
- Professional presentation meeting formatting and length requirements
- Proofreading eliminating mechanical errors undermining credibility
Maintaining Perspective and Balance
Pursuing honors shouldn’t compromise overall wellbeing:
Healthy Academic Ambition
Successful students maintain sustainability:
- Recognize that honors represent achievement recognition, not identity definition
- Balance academic focus with social connection and extracurricular engagement
- Accept that occasional less-than-perfect grades don’t eliminate honors possibility
- Seek help when struggling rather than suffering silently
- Maintain perspective that learning matters beyond grades alone

Rich multimedia profiles balance comprehensive achievement documentation with scannable formatting enabling quick orientation
Mental Health Priority
Academic excellence requires protecting wellbeing:
- Regular sleep prioritized over all-night study sessions
- Healthy eating and exercise maintaining physical foundation
- Social connections providing support and perspective
- Counseling services when anxiety or depression emerge
- Understanding that health always matters more than any grade or honor
Creating Graduation Honors Recognition Displays: Design Strategies
Schools and universities increasingly recognize that traditional diploma notation alone doesn’t adequately celebrate academic honors or inspire future students.
Physical Recognition Spaces
Dedicated areas showcasing academic excellence:
Academic Honor Walls
Permanent installations documenting honors graduates:
- Latin honors recipients organized by graduation year
- Individual name plaques or etched glass panels
- Prominent locations (main entrance lobbies, academic buildings, libraries)
- Distinction between different honor levels through visual hierarchy
- Historical archives documenting institutional academic tradition
Commencement Recognition
Ceremony elements highlighting honors:
- Special honor cords, stoles, or medallions worn by graduates
- Designated seating sections for honors recipients
- Public announcement of Latin honors during name reading
- Photography opportunities with deans and academic leaders
- Reception programs honoring top academic achievers
Digital Recognition Solutions
Modern platforms overcome traditional limitations:
Unlimited Recognition Capacity
Digital displays eliminate physical space constraints:
- Single touchscreen showcases unlimited students across all years
- No need to remove historical honorees to accommodate current graduates
- Comprehensive searchable archives preserving institutional memory
- Equal prominence for all achievement levels and categories
Rich Multimedia Profiles
Digital systems enable comprehensive recognition:
- Professional photography presenting graduates professionally
- Biographical content contextualizing achievement beyond statistics
- Major, minor, and concentration documentation
- Research thesis titles and abstract summaries
- Graduate school destinations and career paths
- Award and scholarship recognition complementing honors
Interactive Exploration
Touchscreen interfaces engage community members:
- Search functionality locating specific graduates instantly
- Filter by graduation year, honor level, major, or other criteria
- Share features enabling social celebration
- QR code access extending recognition to mobile devices
- Analytics tracking engagement demonstrating program impact
Schools can explore modern recognition platforms through digital recognition display solutions that showcase academic excellence effectively.
Strategic Placement and Visibility
Recognition effectiveness depends significantly on location:
High-Traffic Academic Locations
Optimal placement ensures maximum exposure:
- Main entrance lobbies greeting all campus visitors immediately
- Academic office areas where prospective students tour and current students advise
- Libraries and study spaces surrounding students with excellence examples
- Residential hall common areas in campus living communities
- Dining facilities and student unions reaching entire campus populations
Prospective Student Recruitment
Recognition displays serve recruitment functions:
- Admissions office installation showcasing academic culture during campus tours
- Virtual tour integration for remote prospective families
- Open house and preview day focal points demonstrating excellence commitment
- Social media content featuring recognition displays building reputation
- Marketing materials incorporating recognition imagery communicating priorities
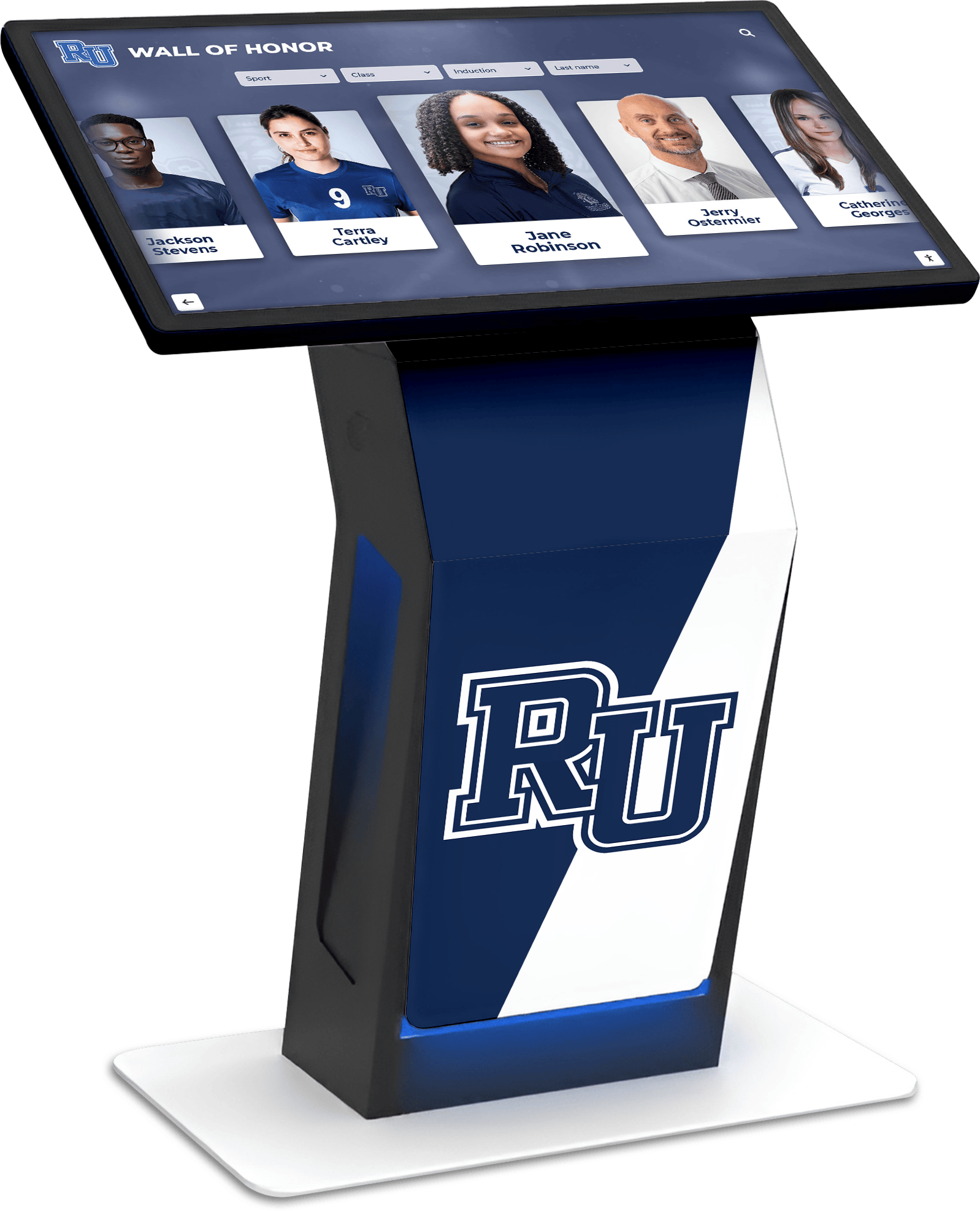

Purpose-built recognition platforms provide professional interfaces optimized specifically for celebrating academic achievement
Addressing Controversies and Concerns About Graduation Honors
Despite widespread use, graduation honors systems face legitimate criticism requiring thoughtful consideration.
Grade Inflation Concerns
Critics argue honors have become less meaningful as grade distributions shift upward:
The Grade Inflation Reality
Studies document substantial grade increases over recent decades:
- Average college GPA rose from approximately 2.9 in 1980s to 3.3+ currently
- Percentage of A grades increased from roughly 35% to over 45% at many institutions
- Honor designations now recognize higher percentages of graduates than historically
- Competitive pressure and student expectations influence grading practices
- Institutional reputation concerns incentivize grade generosity
Institutional Responses
Schools address inflation through various approaches:
- Percentile-based systems automatically adjusting for grade distribution shifts
- More selective honors thresholds (higher GPA requirements, lower percentages recognized)
- Additional requirements beyond grades (thesis, comprehensive exams)
- Contextual transcript notation showing course grade distributions
- Standardized testing requirements demonstrating absolute achievement levels
Equity and Access Questions
Honor systems may inadvertently disadvantage certain student populations:
Systemic Barriers
Critics identify structural inequities:
- First-generation college students lacking cultural knowledge about honors importance and strategies
- Students working substantial hours for financial necessity having less study time available
- Students from under-resourced high schools arriving less prepared for rigorous coursework
- Transfer students whose credits don’t count toward institutional honors GPA
- Non-traditional students balancing family responsibilities alongside coursework
Inclusive Recognition Approaches
Progressive institutions implement more equitable systems:
- Multiple recognition pathways beyond cumulative GPA alone
- Growth and improvement awards acknowledging progress from different starting points
- Financial need-based research stipends enabling thesis completion without work conflicts
- Transfer student modified honors eligibility after institutional residency requirement
- Holistic evaluation considering context and barriers overcome
Discover inclusive recognition in teacher recognition programs that celebrate diverse excellence.
The Overemphasis on GPA Debate
Some educators question whether GPA-centric honors align with learning goals:
Learning vs. Achievement Orientation
Concerns include:
- Grade focus potentially undermining intrinsic learning motivation
- Risk-averse course selection avoiding challenge to protect GPA
- Collaborative learning disincentivized by competitive grading
- Narrow definition of excellence excluding important capabilities
- Stress and mental health impacts of intense GPA pressure
Broader Excellence Recognition
Alternative approaches complement traditional honors:
- Research and creative achievement recognition independent of grades
- Leadership and service awards honoring contribution beyond academics
- Interdisciplinary collaboration recognition valuing teamwork
- Teaching and mentorship excellence awards for peer education
- Real-world impact recognition for applied learning and community engagement
These complementary systems acknowledge that genuine excellence encompasses dimensions not captured by cumulative GPA alone.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Academic Excellence Recognition
Graduation honors—from cum laude through magna to summa cum laude—represent centuries of academic tradition recognizing exceptional scholarly achievement through standardized, internationally recognized designations. These Latin phrases carry consistent meaning across institutions, time periods, and geographical boundaries, providing validated markers distinguishing outstanding students while motivating peers toward excellence.
Understanding graduation honors levels enables students to pursue these prestigious recognitions strategically while helping educators design equitable systems celebrating achievement appropriately. From calculation methodologies and institutional variations through modern recognition technologies and ongoing controversies, comprehensive knowledge of honors systems informs better educational practices serving all students effectively.
Transform Your Academic Recognition Program
Discover how modern digital recognition solutions can help your institution celebrate graduation honors, Latin distinctions, and academic excellence through engaging displays that inspire entire educational communities.
Explore Recognition SolutionsContemporary schools increasingly recognize that meaningful academic recognition extends beyond traditional honors to encompass multiple achievement dimensions—from sustained honor roll status and subject-specific excellence through research accomplishment and growth trajectories. Digital recognition platforms enable comprehensive celebration impossible with limited physical plaques or static displays, creating engaging touchscreen experiences that showcase unlimited scholars while making excellence visible and inspirational throughout educational communities.
Whether your institution uses traditional Latin honors, develops custom recognition tiers, or implements comprehensive multi-dimensional achievement systems, the core principle remains consistent: recognizing academic excellence motivates continued achievement, strengthens educational culture, and honors the sustained dedication distinguishing exceptional scholars from peers. Modern technology simply enables celebration at scale previously impossible, ensuring every deserving student receives lasting recognition their accomplishments merit.
Ready to elevate your academic recognition? Explore comprehensive recognition approaches, discover student achievement display strategies, and learn how interactive technology solutions can transform how your institution celebrates the academic excellence that defines educational mission and inspires future generations of scholars.