School facilities management has evolved from basic custodial services and reactive repairs into a strategic discipline directly impacting student achievement, teacher effectiveness, and community perception. Research consistently demonstrates that well-maintained, thoughtfully designed school environments correlate with improved academic outcomes, higher attendance rates, and enhanced recruitment of quality educators. Yet many districts struggle to balance competing demands—aging infrastructure requiring substantial investment, limited budgets constraining improvement initiatives, and evolving educational models demanding flexible, technology-rich spaces.
The stakes extend beyond aesthetics and comfort. Facility conditions influence everything from air quality affecting student concentration to security systems protecting community safety, energy efficiency determining budget allocation flexibility, and common area design shaping school culture. Modern facilities directors must serve as strategic partners in educational mission fulfillment rather than simply maintaining physical plants—requiring comprehensive approaches integrating preventive maintenance, technology adoption, sustainability practices, and stakeholder engagement.
This comprehensive guide explores evidence-based strategies for effective school facilities management, from preventive maintenance systems and technology integration through sustainability initiatives and creating environments that celebrate achievement while supporting learning. Whether managing elementary buildings, comprehensive high school campuses, or district-wide facilities portfolios, these approaches provide frameworks for operational excellence that advances educational outcomes while demonstrating responsible stewardship of community resources.
Modern school facilities management demands proactive, strategic approaches that prevent problems before they disrupt learning environments, integrate technology that enhances both operations and education, and create spaces that inspire students while supporting diverse instructional methods. The transition from reactive “fix it when it breaks” mentality to comprehensive facilities stewardship transforms buildings from simple containers for education into active contributors to learning success.

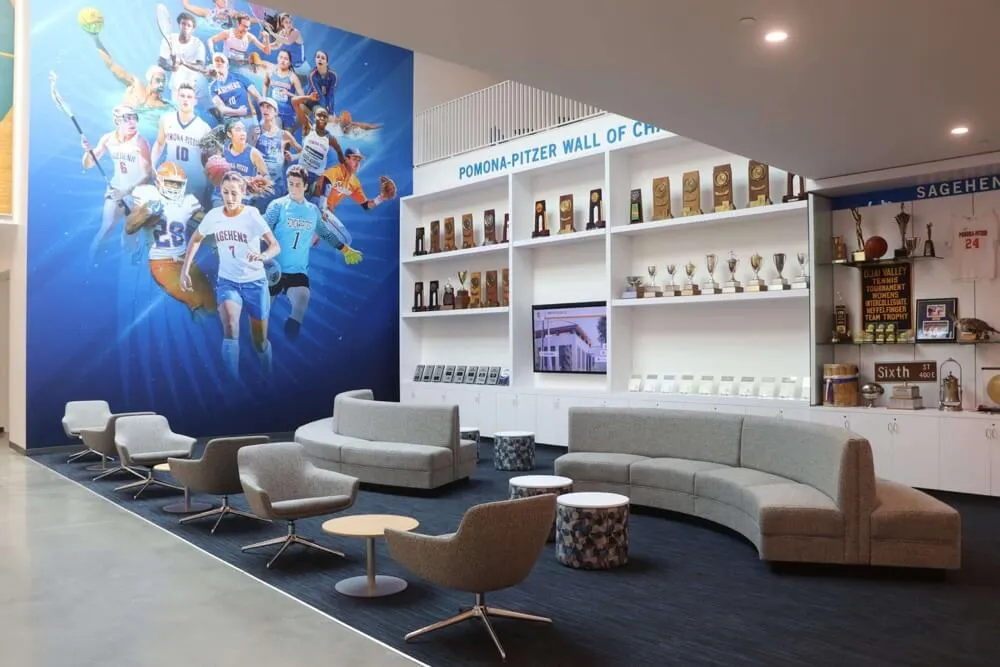
Modern facilities integrate technology and contemporary design creating environments that inspire learning while showcasing institutional pride
The Strategic Role of Facilities Management in Educational Success
Understanding how facility conditions directly influence educational outcomes elevates facilities management from operational necessity to strategic priority deserving appropriate investment and attention.
Research Connecting Facility Quality to Academic Achievement
Extensive research establishes clear relationships between building conditions and student performance that should inform facility investment decisions:
Academic Performance Correlations
Multiple studies demonstrate measurable academic impacts from facility improvements:
- Schools with excellent facility conditions show 10-11% higher test scores compared to poor-condition facilities, according to research published in the Journal of Educational Administration
- Improved indoor air quality correlates with 8-15% increases in standardized test performance
- Adequate lighting conditions improve reading speed and comprehension by 15-20%
- Temperature control within optimal ranges (68-74°F) significantly impacts student concentration and task completion
- Acoustical treatments reducing ambient noise increase learning retention by 10-30%
These correlations demonstrate that facility investments deliver tangible returns beyond building preservation—they directly support educational mission achievement through environments optimized for learning.
Teacher Recruitment and Retention Effects
Facility quality significantly influences educator decisions about employment:
- Teachers consistently cite building conditions as important factors in school selection decisions
- Modern, well-maintained facilities communicate institutional respect for educators and their work
- Technology-rich environments attract educators comfortable with innovative instructional methods
- Adequate workspace, functional equipment, and comfortable conditions reduce stress and burnout
- Schools with poor facility conditions experience 20-30% higher teacher turnover rates
In competitive educator labor markets, facility quality provides recruitment advantages while protecting investments in professional development through improved retention.
Community Perception and Enrollment Impact
School facilities serve as visible representations of educational quality and community investment:
First Impression Formation
Prospective families form lasting impressions during initial campus encounters:
- Building exteriors and entry areas communicate institutional priorities and investment levels
- Clean, well-maintained spaces suggest organizational competence and attention to detail
- Modern technology integration signals commitment to contemporary educational approaches
- Recognition displays and celebration of achievement demonstrate institutional pride
- Accessibility features communicate inclusive values and legal compliance

Welcoming entrance areas with integrated technology create positive first impressions for prospective families
Competitive Positioning Effects
In districts with school choice or private school competition, facility quality directly influences enrollment:
- Facilities represent tangible evidence supporting marketing claims about educational quality
- Modern environments attract families prioritizing contemporary educational experiences
- Community spaces demonstrating institutional pride build emotional connections
- Safety features and accessibility accommodations address practical parent concerns
- Technology infrastructure signals preparedness for digital-age learning
Schools competing for enrollment must recognize facility conditions as enrollment drivers requiring strategic investment rather than deferred maintenance accumulation.
Developing Comprehensive Preventive Maintenance Programs
Shifting from reactive repairs to systematic preventive maintenance reduces long-term costs while minimizing disruptions that compromise educational environments.
Creating Facility Assessment and Inventory Systems
Effective preventive maintenance begins with comprehensive understanding of existing conditions and maintenance requirements:
Complete Asset Inventory Development
Systematic cataloging provides the foundation for maintenance planning:
- Comprehensive equipment and system inventories documenting all maintainable assets
- Age and condition assessments establishing replacement planning priorities
- Warranty and service contract documentation ensuring obligation fulfillment
- Manufacturer specifications and maintenance requirements for each system
- Critical system identification determining backup and emergency protocols
- Parts inventory management ensuring repair capability without extended downtime
Districts implementing computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) report 30-40% improvements in maintenance efficiency through systematic asset tracking and automated work order management.
Facility Condition Assessment Protocols
Regular assessment identifies emerging problems before they escalate:
- Annual comprehensive facility walkthroughs examining all systems and spaces
- Quarterly focused inspections on critical systems (HVAC, roofing, safety equipment)
- Monthly quick-check inspections identifying obvious problems requiring immediate attention
- Standardized assessment forms ensuring consistency across buildings and personnel
- Photographic documentation tracking condition changes over time
- Condition scoring systems quantifying facility states enabling data-driven prioritization
These systematic assessments transform vague awareness of “things needing attention” into quantified inventories supporting evidence-based investment decisions and budget justification.

Comprehensive facility maintenance extends to all building elements including environmental design and technology integration
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling and Execution
Systematic scheduling ensures consistent maintenance execution preventing breakdown that disrupts education:
Time-Based Maintenance Calendars
Scheduled maintenance organized around calendar cycles ensures nothing gets overlooked:
- Daily tasks (trash removal, restroom checks, safety inspections, common area cleaning)
- Weekly activities (floor maintenance, HVAC filter checks, grounds maintenance, supply restocking)
- Monthly responsibilities (deep cleaning rotations, equipment lubrication, safety equipment testing)
- Quarterly requirements (HVAC system servicing, roof inspections, playground equipment safety checks)
- Annual obligations (fire system certification, boiler inspection, comprehensive facility assessment)
Calendar-based systems prevent the “squeaky wheel” problem where only obvious problems receive attention while less-visible but equally important maintenance gets deferred until expensive failures occur.
Condition-Based Maintenance Strategies
Beyond fixed schedules, monitoring actual system conditions enables optimized maintenance timing:
- Performance monitoring identifying efficiency declines suggesting service needs
- Vibration analysis predicting mechanical system failures before breakdown
- Temperature monitoring revealing HVAC performance degradation
- Water quality testing preventing plumbing system problems
- Predictive analytics using historical data to optimize maintenance intervals
Condition-based approaches prevent unnecessary maintenance while catching problems early—balancing efficiency with reliability that educational environments require.
Summer Maintenance Windows
Strategic timing concentrates disruptive maintenance during breaks:
- Major projects (flooring replacement, painting, infrastructure upgrades) scheduled during extended breaks
- HVAC system servicing completed before cooling season demands
- Technology infrastructure updates occurring when disruption doesn’t affect instruction
- Deep cleaning and restoration work impossible during occupied periods
- Preventive maintenance requiring extended system shutdowns timed to minimize impact
Schools maximizing summer maintenance windows report 40-60% reductions in instructional disruptions from facility work while maintaining higher overall building conditions through concentrated effort periods.
Technology Integration in Facilities Management
Modern technology dramatically enhances facilities management efficiency while enabling capabilities impossible through manual processes alone.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)
CMMS platforms transform facilities management from paper-based chaos into systematic, data-driven operations:
Core CMMS Capabilities
Effective systems provide comprehensive functionality supporting all maintenance operations:
- Work order management streamlining request submission, assignment, tracking, and completion documentation
- Asset management maintaining complete equipment inventories with service histories
- Preventive maintenance scheduling automating routine task assignment and tracking
- Inventory management monitoring parts and supplies preventing stockouts
- Labor tracking documenting maintenance staff time allocation and productivity
- Cost tracking enabling accurate expense allocation and budget forecasting
- Reporting and analytics providing performance metrics and operational insights
Districts implementing CMMS platforms report 25-35% improvements in maintenance efficiency through better organization, reduced duplicated effort, and data-driven process optimization.
Mobile Access and Real-Time Updates
Modern CMMS solutions provide mobile applications transforming field operations:
- Maintenance staff receive and update work orders via smartphones or tablets in real-time
- Photo documentation captured on-site immediately without returning to offices
- Parts and supply needs identified and ordered directly from job locations
- Equipment service histories accessed in the field informing repair decisions
- Real-time status updates keeping requestors informed about progress
Mobile capabilities eliminate the delays and information gaps inherent in paper-based systems where work orders physically travel between offices, work sites, and filing cabinets.
Building Automation and Smart Systems
Intelligent building systems optimize operations while reducing energy costs and improving occupant comfort:
HVAC Automation and Optimization
Smart HVAC controls deliver substantial operational improvements:
- Occupancy-based scheduling ensuring conditioning only when spaces are used
- Temperature optimization balancing comfort with energy efficiency
- Remote monitoring and adjustment from central locations or mobile devices
- Predictive maintenance alerts based on performance degradation patterns
- Zone-level control providing targeted conditioning rather than whole-building approaches
- Integration with weather forecasts optimizing pre-cooling or pre-heating strategies
Schools implementing advanced HVAC automation report 15-30% energy cost reductions while improving temperature consistency and comfort compared to manual or basic programmable systems.
Lighting Management Systems
Intelligent lighting controls enhance efficiency while improving environments:
- Occupancy sensors automatically controlling lights in intermittently used spaces
- Daylight harvesting dimming artificial lighting when natural light is adequate
- Scheduled controls matching lighting to known occupancy patterns
- Centralized management enabling campus-wide adjustments from single interfaces
- Emergency override capabilities ensuring safety during unusual circumstances
Modern lighting systems reduce energy consumption by 30-50% compared to manually controlled systems while improving consistency and extending lamp life through optimized operation.

Technology integration extends beyond operational systems to include interactive displays that enhance school environment while supporting recognition programs
Security and Access Control Technology
Modern security systems protect students and staff while providing operational efficiency:
Integrated Access Control Systems
Electronic access management enhances both security and convenience:
- Card or biometric-based access eliminating traditional keys that are easily lost or copied
- Time-based access permissions automatically granting or denying entry based on schedules
- Remote lockdown capabilities enabling instant security response
- Entry logging documenting who accessed which areas when for accountability
- Integration with other systems (fire alarms automatically unlocking emergency exits)
- Visitor management systems tracking and controlling non-staff campus presence
Schools implementing comprehensive access control report improved security while dramatically reducing locksmith expenses from lost keys and lock changes.
Video Surveillance Integration
Modern camera systems provide security enhancement while supporting operations:
- High-definition coverage of entrances, hallways, parking areas, and common spaces
- Remote viewing enabling administrators to assess situations without physical presence
- Motion-detection recording conserving storage while capturing relevant events
- Integration with access control systems correlating video with entry attempts
- Analytics identifying unusual patterns or unauthorized presence
- Evidence documentation supporting investigations when incidents occur
Beyond security applications, video systems help facilities managers remotely assess building conditions, verify completion of maintenance tasks, and understand how spaces are actually used informing improvement planning.
Creating Recognition-Rich School Environments
Modern school facilities should celebrate achievement and foster pride through thoughtful design and strategic technology integration that showcases institutional excellence.
Strategic Placement of Recognition Displays
Common areas and high-traffic locations provide opportunities for highlighting achievement:
Lobby and Entrance Recognition
School entry areas establish immediate impressions while celebrating community:
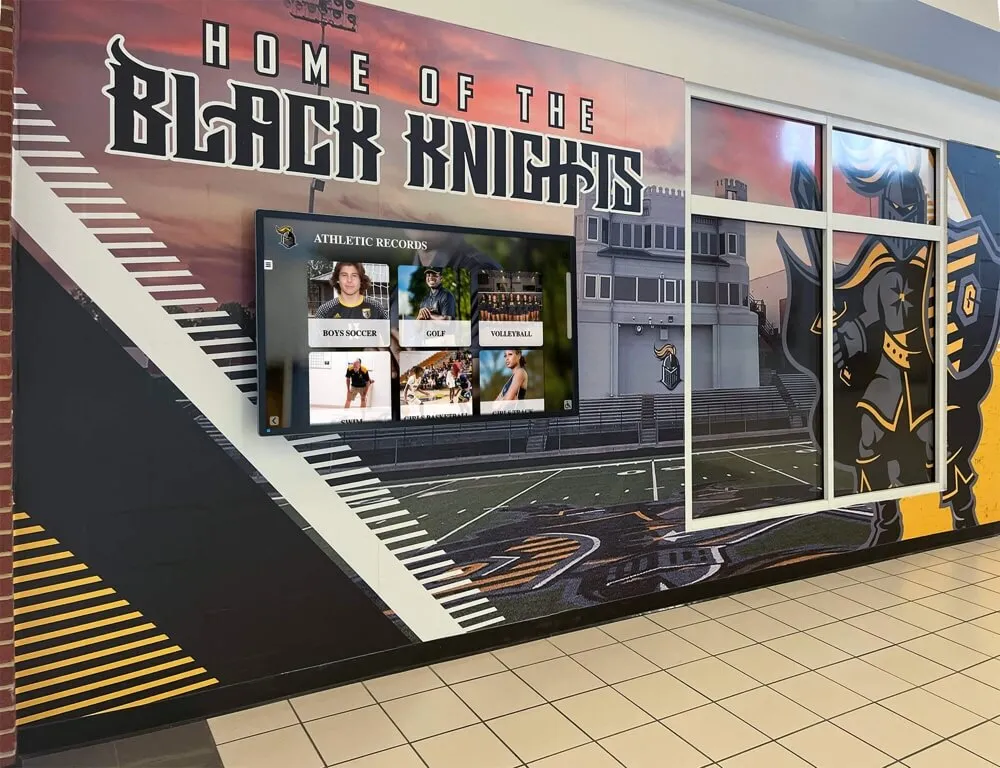
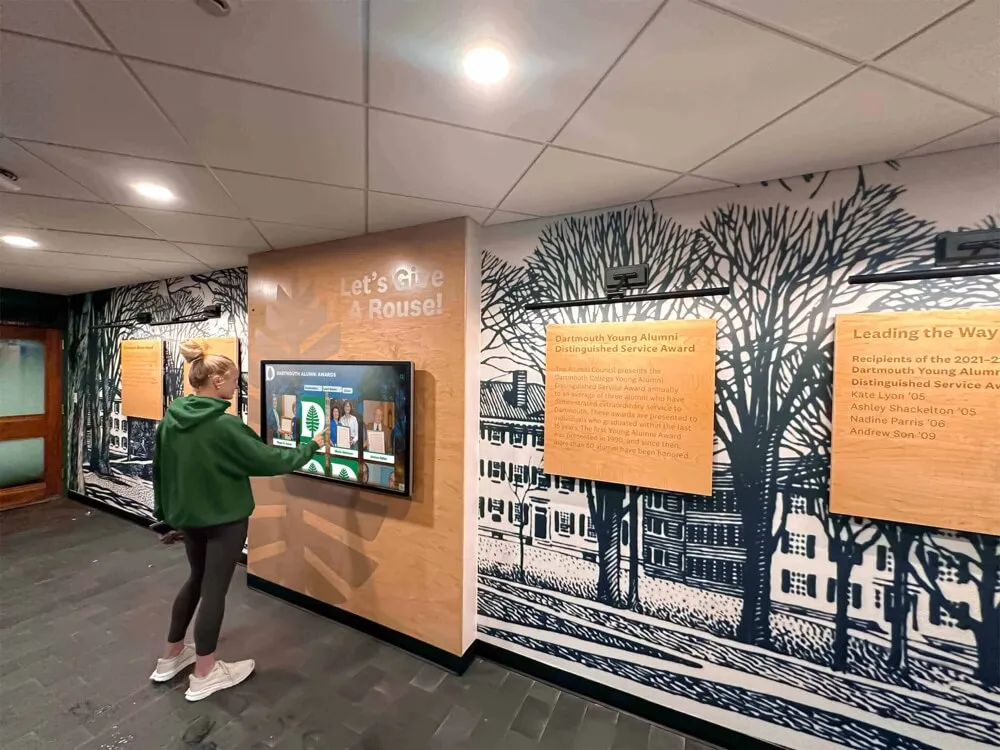
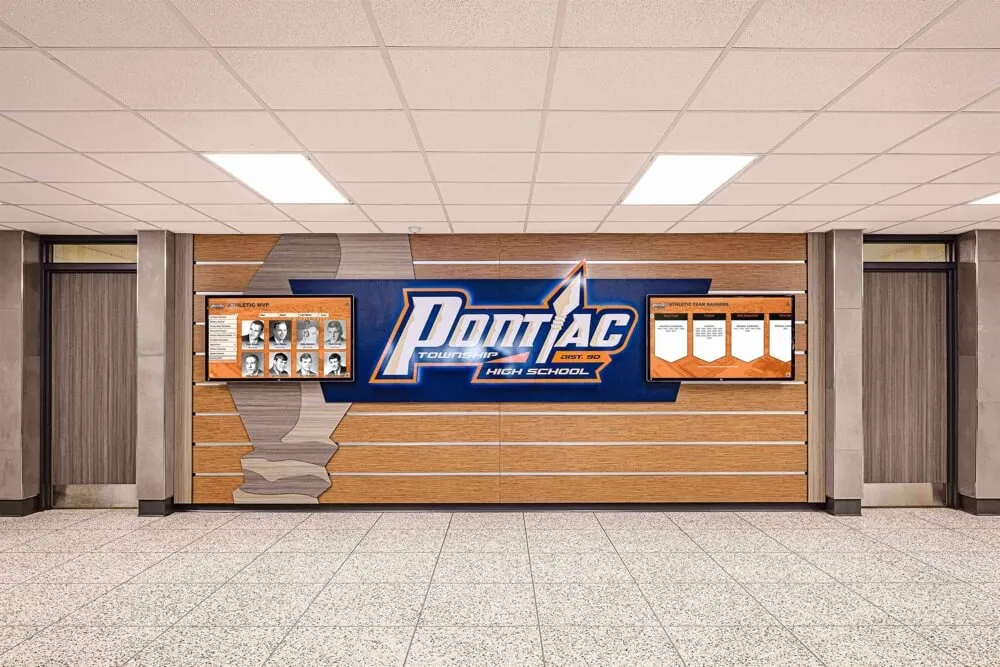
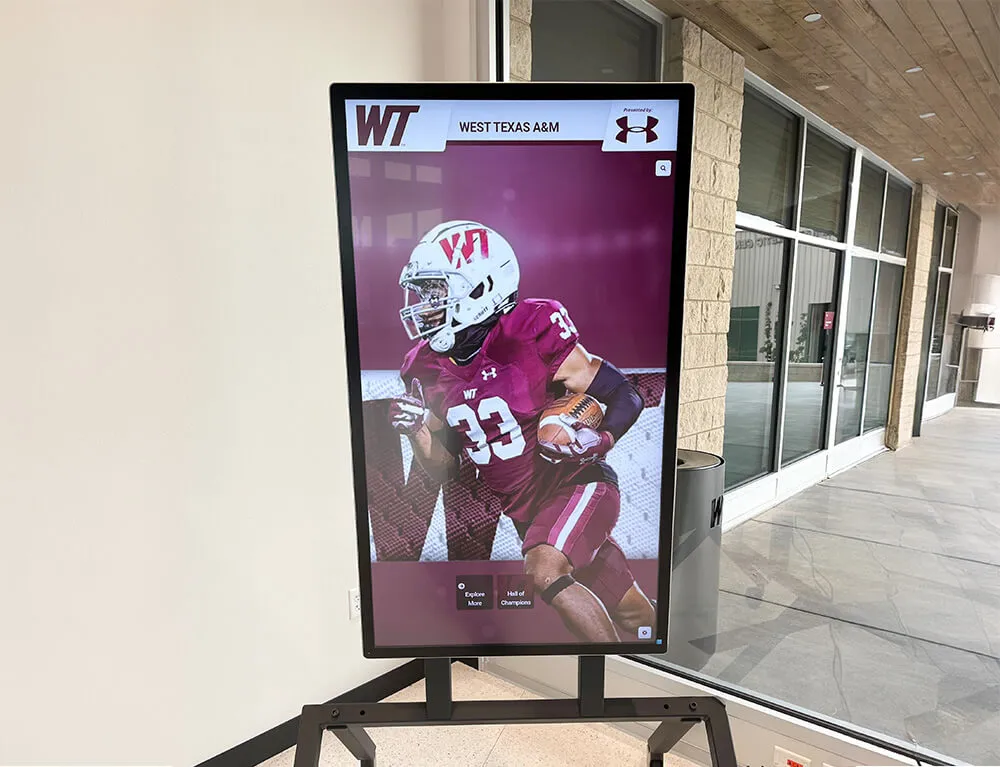
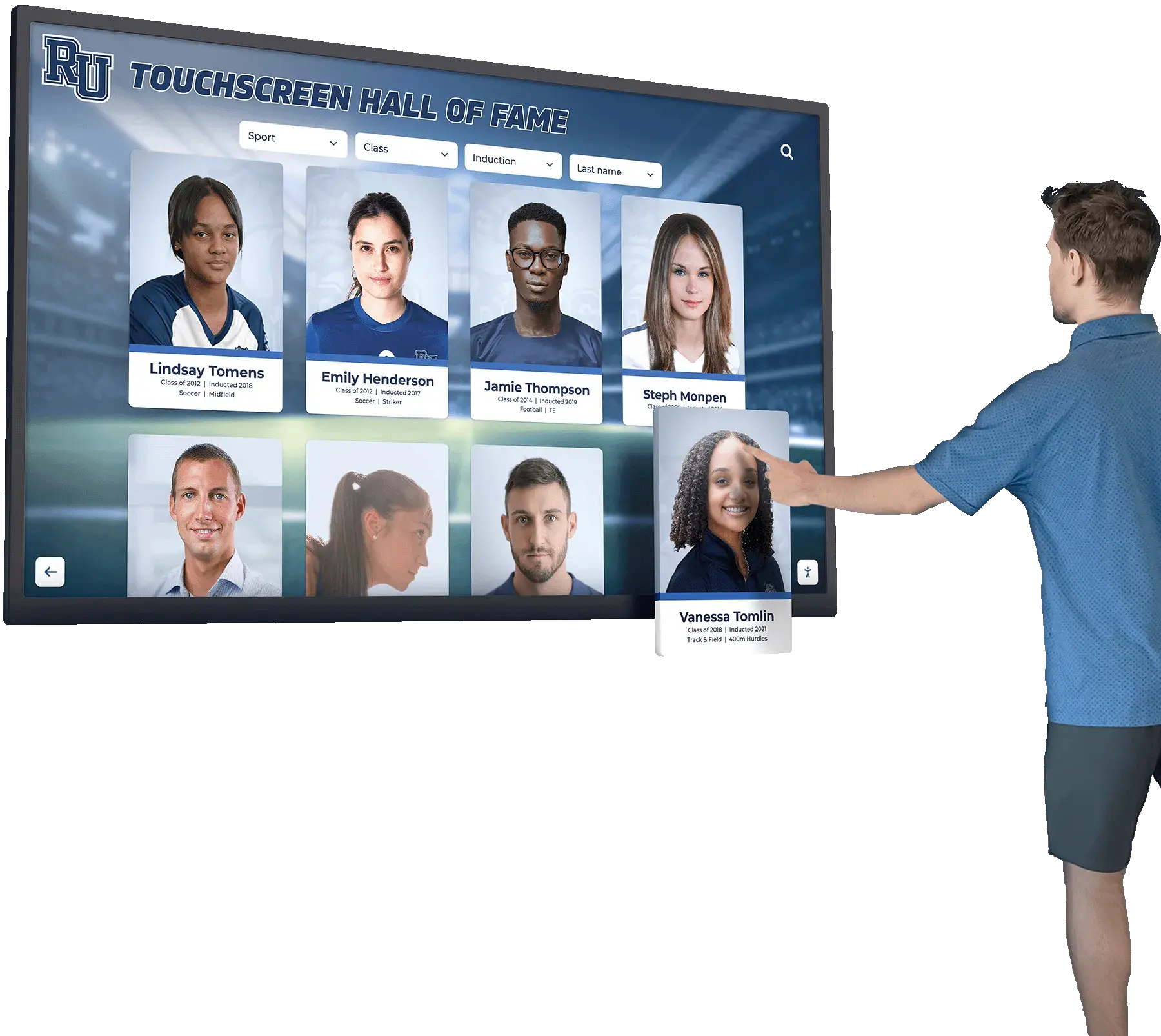
- Digital recognition displays in main lobbies showcasing academic, athletic, and extracurricular achievements
- Interactive touchscreens enabling visitors to explore institutional history and accomplishments
- Automated content updates ensuring recognition remains current without maintenance burden
- Unlimited capacity overcoming space constraints limiting traditional plaque approaches
- Multimedia integration incorporating photos, videos, and comprehensive biographical content
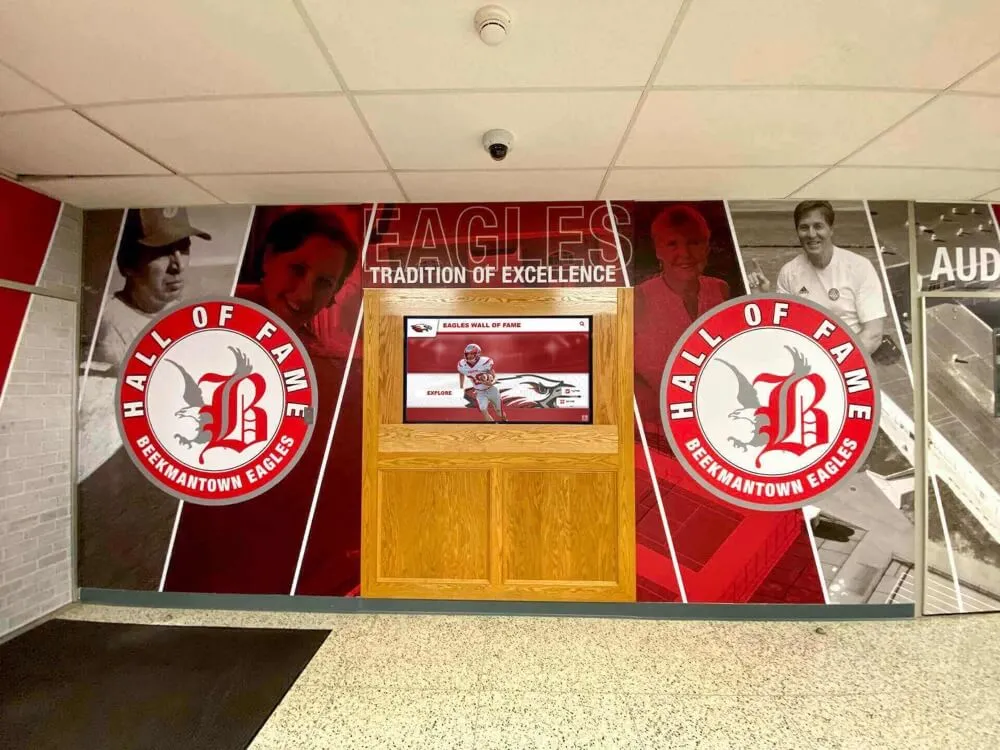
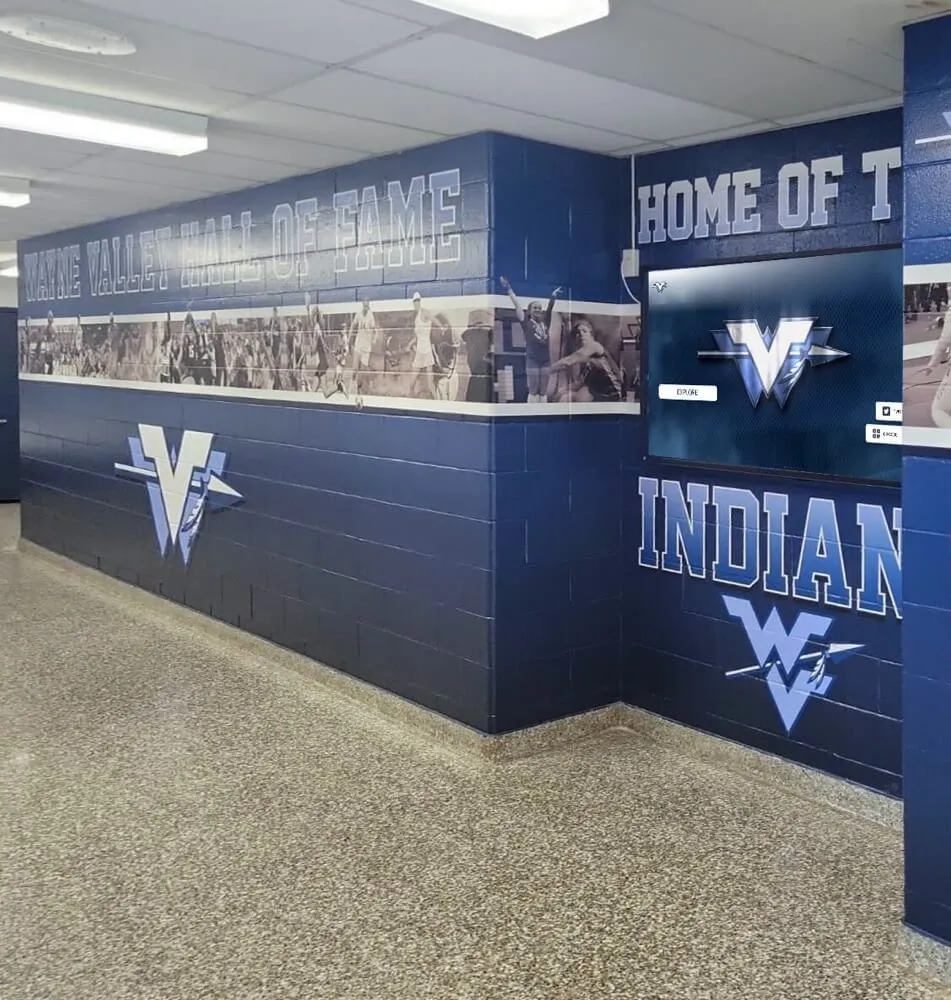
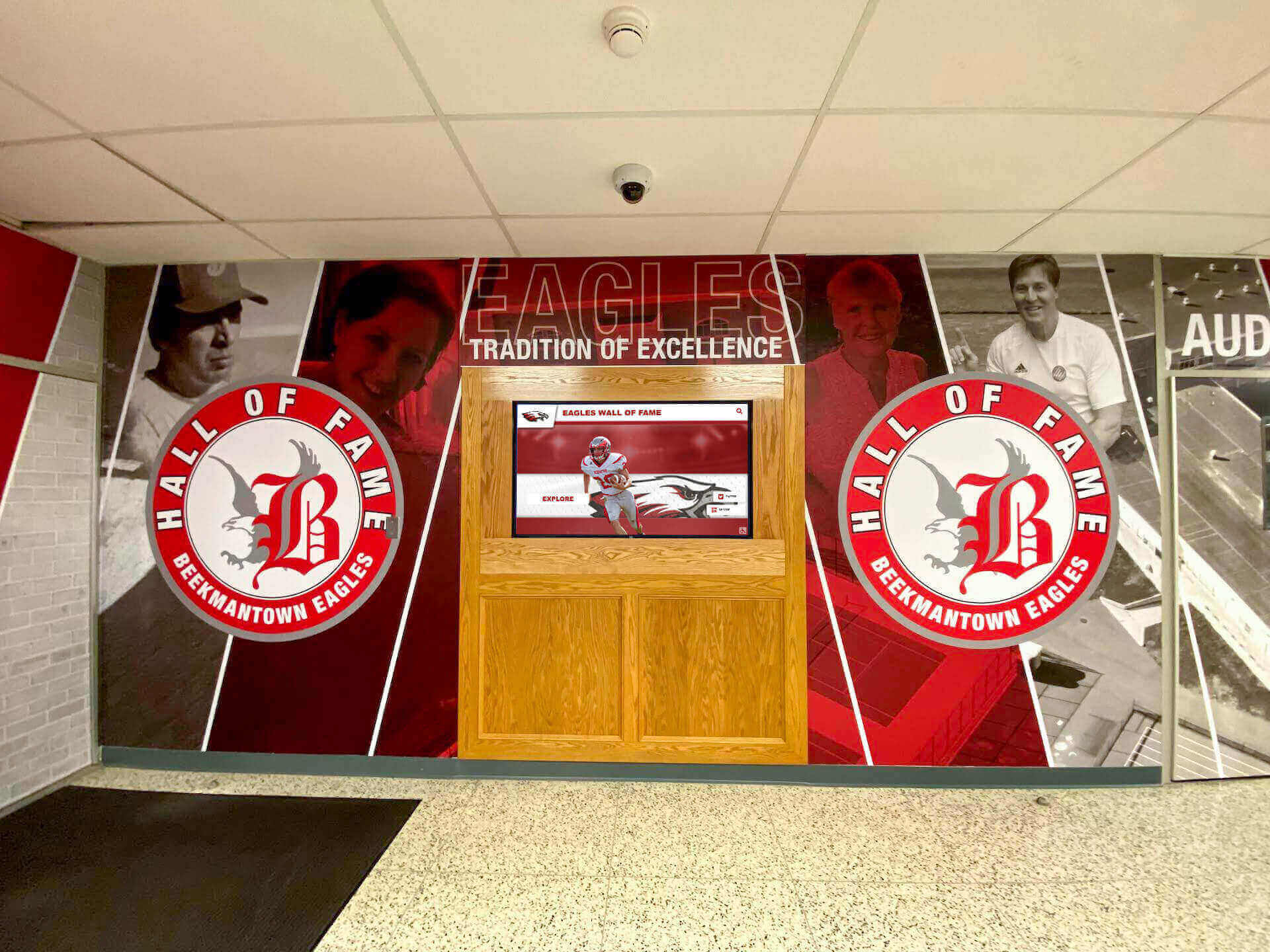
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions transform traditional trophy cases and plaque walls into dynamic recognition systems that engage visitors while demonstrating institutional commitment to celebrating excellence. These modern displays integrate seamlessly into facility improvement initiatives while addressing the digital recognition component of contemporary school environments.
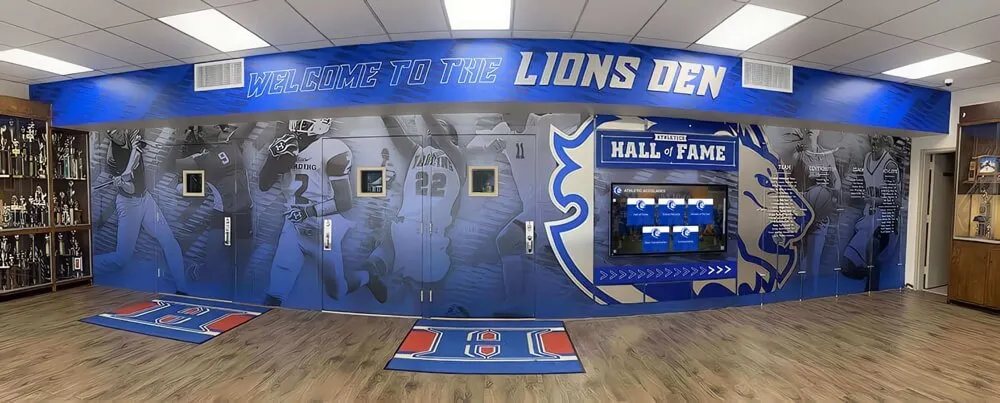
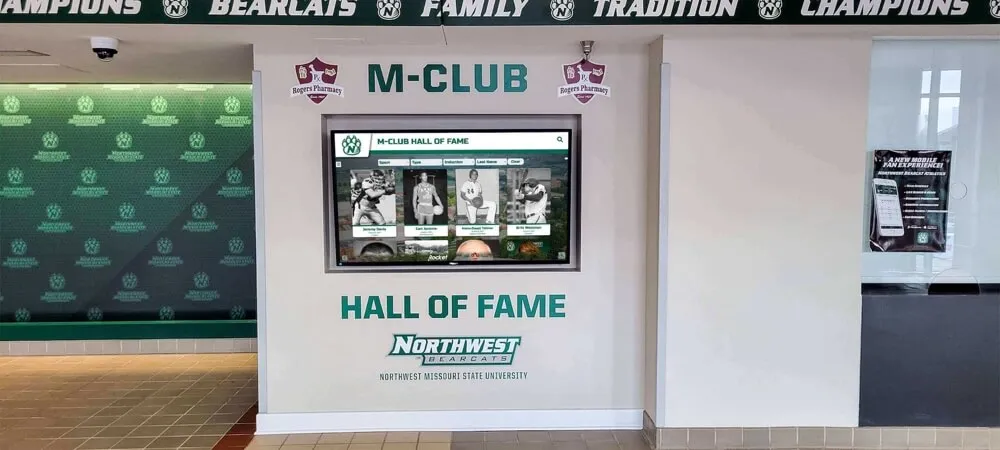
Athletic Facility Recognition
Sports venues provide natural locations for celebrating competitive achievement:
- Record boards displaying current school, conference, and individual achievement records
- Championship recognition highlighting team and individual titles
- Digital trophy cases combining traditional trophies with digital content
- Video highlight integration showing memorable performances and achievements
- Team history archives preserving institutional athletic tradition
Athletic recognition demonstrates program excellence while building pride among current students, alumni, and community members who take ownership in competitive success.
Academic Recognition Integration
Intellectual achievement deserves visibility equal to athletic accomplishment:
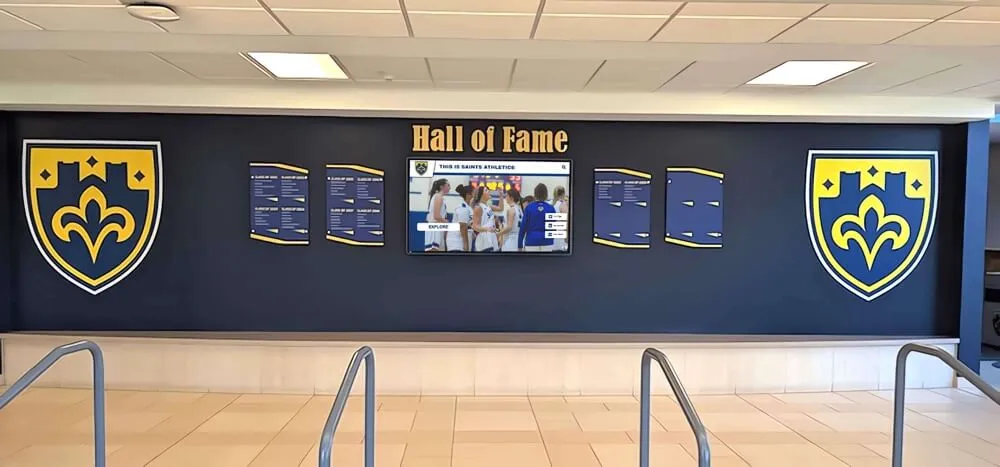
Honor Roll and Academic Excellence Displays
Systematic academic recognition creates achievement-oriented cultures:
- Digital academic recognition boards showcasing honor students and academic awards
- Searchable databases enabling students and families to find individual recognition
- Multiple recognition categories beyond GPA including improvement, subject excellence, and special achievements
- Term-based updates ensuring current achievement receives prominence
- Historical archives preserving institutional academic tradition

Academic recognition displays demonstrate institutional priorities while motivating student achievement through visible celebration of excellence
Making intellectual achievement as visible as athletic success shapes institutional culture while providing motivation extending beyond traditionally high-achieving students to all learners seeing peers celebrated for educational excellence.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency Initiatives
Environmental responsibility and operational cost reduction align in comprehensive sustainability programs that benefit budgets while demonstrating community stewardship.
Energy Management and Consumption Reduction
Systematic approaches to energy management deliver measurable financial and environmental returns:
Comprehensive Energy Audits
Understanding current consumption provides baselines and identifies opportunities:
- Professional energy assessments examining all building systems and usage patterns
- Utility data analysis identifying consumption trends and anomalies
- Benchmarking comparing facilities to similar schools revealing relative efficiency
- System-by-system assessment quantifying improvement opportunities
- Investment analysis calculating payback periods for proposed improvements
- Prioritized recommendation lists balancing impact with implementation cost
Schools implementing audit recommendations typically achieve 15-30% energy cost reductions within 2-3 years with projects paying for themselves through savings then delivering ongoing budget relief.
HVAC Efficiency Improvements
Heating and cooling typically represent 40-60% of school energy costs making HVAC optimization high-impact:
- Regular maintenance ensuring systems operate at design efficiency
- Filter management maintaining airflow while protecting equipment
- Control strategy optimization balancing comfort with efficiency
- Variable frequency drives on motors reducing energy consumption
- High-efficiency equipment replacement when existing systems reach end-of-life
- Building envelope improvements reducing conditioning loads
HVAC improvements often deliver fastest payback among energy initiatives while simultaneously improving occupant comfort and reducing maintenance costs through more reliable, modern equipment.
Lighting Modernization
LED lighting retrofits provide dramatic savings with short payback periods:
- LED technology uses 50-75% less energy than traditional fluorescent and incandescent lighting
- Longer lamp life (50,000-100,000 hours) dramatically reduces maintenance requirements
- Improved light quality enhancing visibility and reducing eye strain
- Instant-on capability eliminating warmup delays
- Integration with control systems enabling optimization impossible with older technology
Many utilities offer incentive programs subsidizing lighting retrofits, further improving already attractive financial returns while advancing sustainability goals.

Energy-efficient lighting and modern systems reduce operational costs while creating better environments for learning and recognition
Water Conservation and Management
Water and wastewater costs represent significant operational expenses addressable through conservation initiatives:
Fixture and Equipment Efficiency
Modern plumbing fixtures dramatically reduce consumption:
- Low-flow faucets and toilets reducing consumption by 30-50% compared to older fixtures
- Sensor-activated fixtures eliminating water waste from fixtures left running
- Efficient irrigation systems with weather-based controls preventing overwatering
- Leak detection systems identifying hidden problems before substantial waste occurs
- Water-efficient kitchen equipment in food service areas
Water efficiency improvements typically pay for themselves within 3-7 years through reduced utility costs while demonstrating environmental stewardship.
Stormwater Management
Sustainable stormwater approaches reduce infrastructure costs while providing environmental benefits:
- Rain gardens and bioswales capturing runoff naturally
- Permeable pavement reducing runoff volume and velocity
- Green roofs on appropriate buildings providing multiple benefits
- Rainwater harvesting for irrigation reducing potable water consumption
- Native landscaping reducing irrigation requirements while supporting local ecosystems
Beyond operational benefits, visible sustainability features provide learning opportunities connecting environmental concepts to practical applications students observe daily.
Indoor Environmental Quality and Health
Building environments directly impact occupant health, comfort, and performance making indoor environmental quality a critical facilities management consideration.
Air Quality Management
Maintaining healthy indoor air requires systematic attention to multiple factors:
Ventilation and Fresh Air Exchange
Adequate ventilation prevents pollutant accumulation and controls humidity:
- HVAC systems providing recommended outdoor air exchange rates
- Regular filter replacement maintaining air quality while protecting equipment
- Humidity control preventing mold growth and maintaining comfort (30-50% relative humidity)
- Carbon dioxide monitoring ensuring adequate air exchange in occupied spaces
- Ventilation rate increases during high-occupancy periods and activities generating pollutants
Research demonstrates that improved ventilation correlates with reduced illness-related absences, improved concentration, and better test performance—making air quality investments that support educational outcomes.
Source Control and Material Selection
Preventing pollutant introduction proves more effective than removal:
- Low-VOC (volatile organic compound) materials in cleaning products, paints, and adhesives
- Furniture and fixture selection prioritizing low-emission products
- Flooring materials avoiding vinyl chloride and other problematic compounds
- Integrated pest management minimizing pesticide use
- Construction and renovation protocols isolating work areas and providing curing periods before occupancy
Material selection during renovations and purchasing decisions continuously improves building environments while demonstrating health prioritization.
Acoustic Environment Optimization
Noise significantly impacts learning requiring thoughtful acoustic design:
Sound Control Strategies
Multiple approaches combine to create appropriate acoustic environments:
- Ceiling tiles with high Noise Reduction Coefficient (NRC) ratings absorbing sound
- Carpet and soft furnishings reducing reverberation
- Equipment selection prioritizing quiet operation (HVAC systems, technology)
- Space planning separating noisy activities from areas requiring concentration
- Sound masking systems in open office areas protecting conversations
- Behavioral expectations and enforcement regarding appropriate noise levels
Teachers consistently cite excessive noise as significant barriers to effective instruction making acoustic improvements that directly support teaching and learning.

Thoughtfully designed spaces balance acoustic control, visual appeal, and recognition elements creating supportive environments for learning and community
Safety and Security Infrastructure
Comprehensive safety systems protect occupants while supporting emergency response capabilities schools hope never to need but must maintain continuously.
Emergency Preparedness Systems
Modern schools require integrated systems supporting various emergency scenarios:
Communication and Notification Systems
Rapid, reliable communication proves essential during emergencies:
- PA systems reaching all building areas with clear, intelligible announcements
- Mass notification capabilities sending emergency alerts to staff mobile devices
- Visual alert systems supplementing audio for hearing-impaired occupants and noisy environments
- Weather alert integration providing automatic warnings of severe conditions
- Integration with local emergency services enabling two-way communication
- Regular testing ensuring systems function when needed
Communication system reliability during actual emergencies depends on regular testing, maintenance, and training ensuring staff and students know how to interpret and respond to various alerts.
Lockdown and Shelter Capabilities
Physical security features support emergency response protocols:
- Lockable classroom doors controllable from inside rooms without hall access
- Window coverings enabling visibility control during lockdown situations
- Hardened entry points at main building access locations
- Safe areas for shelter during severe weather events
- Emergency supply kits in classrooms and common areas
- Backup power ensuring critical systems operate during extended outages
Security infrastructure investments balance protection with maintaining welcoming, accessible environments that support normal operations—avoiding fortress-like designs that harm school culture while implementing reasonable precautions.
Visitor Management and Access Control
Knowing who is on campus and controlling access to appropriate areas enhances security:
Check-In and Identification Systems
Systematic visitor management provides security and documentation:
- Required check-in at single, controlled entry points during school hours
- Photo identification scanning and visitor badge printing
- Background check integration for volunteers and regular visitors
- Destination logging documenting where visitors are authorized
- Time-limited access controlling duration of campus presence
- Integration with access control systems enabling or restricting door access
Modern visitor management systems automate processes that manual sign-in sheets accomplish poorly while providing security event documentation and deterring inappropriate access through visible management systems.
Custodial and Grounds Maintenance Standards
Facility cleanliness and appearance directly impact learning environments, health outcomes, and community perceptions requiring systematic approaches ensuring consistent quality.
Custodial Operations and Quality Standards
Cleaning programs should follow evidence-based standards ensuring healthy, attractive environments:
Frequency-Based Cleaning Schedules
Different areas and surfaces require different cleaning frequencies:
- Daily tasks (restroom cleaning, trash removal, high-touch surface disinfection, entry area maintenance)
- Weekly activities (floor mopping, dust mopping, low-touch surface cleaning, interior glass cleaning)
- Monthly requirements (high dusting, baseboard cleaning, deep restroom cleaning, detailed furniture cleaning)
- Quarterly projects (floor stripping and waxing, carpet deep cleaning, exterior window washing)
- Annual initiatives (comprehensive deep cleaning, equipment maintenance, inventory assessment)
Systematic schedules ensure nothing gets overlooked while enabling staffing and supply planning supporting consistent execution.
Green Cleaning Programs
Environmentally responsible cleaning protects occupant health while reducing environmental impact:
- Third-party certified green cleaning products meeting health and environmental standards
- Microfiber cleaning systems reducing chemical requirements while improving effectiveness
- HEPA-filtered vacuum systems preventing dust and allergen redistribution
- Proper dilution and application procedures maximizing effectiveness while minimizing chemical use
- Staff training on green cleaning methods and product selection
Schools implementing comprehensive green cleaning programs report improved indoor air quality, reduced chemical exposure complaints, and positive community perception while maintaining or improving cleanliness levels.

Consistent custodial standards maintain attractive, healthy environments supporting learning while showcasing institutional pride
Grounds Maintenance and Landscape Management
Exterior environments create first impressions while providing learning and recreation spaces:
Seasonal Maintenance Programs
Grounds maintenance follows seasonal cycles requiring planning and scheduling:
- Spring activities (cleanup, mulching, planting, irrigation startup, lawn aeration and fertilization)
- Summer tasks (mowing and trimming, irrigation management, pest control, playground maintenance)
- Fall requirements (leaf removal, aeration, overseeding, irrigation winterization, winter preparation)
- Winter duties (snow and ice removal, pathway safety, equipment maintenance, planning for spring)
Proactive seasonal maintenance prevents problems while maintaining attractive, safe exterior environments year-round.
Sustainable Landscape Practices
Modern grounds management balances aesthetics with environmental responsibility:
- Native plant selection reducing irrigation and maintenance requirements
- Integrated pest management minimizing pesticide use
- Organic fertilizer programs supporting soil health
- Mulching and composting reducing waste while improving soil
- Rain gardens and bioswales managing stormwater naturally
- Reduced lawn areas replacing high-maintenance grass with sustainable alternatives
Sustainable landscapes reduce long-term maintenance costs while providing visible demonstrations of environmental stewardship that support educational missions.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication
Effective facilities management requires engaging various stakeholders understanding their needs and communicating facility conditions, improvement plans, and operational decisions.
Internal Stakeholder Communication
Keeping staff and students informed supports smooth operations and addresses concerns proactively:
Maintenance Request Systems
Simple, responsive request processes ensure problems get reported and addressed:
- Easy-to-access request submission (online forms, email, phone, mobile apps)
- Automatic acknowledgment confirming receipt and expected response timeframes
- Status updates keeping requestors informed about progress
- Completion notification closing communication loops
- Feedback mechanisms capturing satisfaction and identifying improvement opportunities
Responsive request systems build trust while ensuring facilities managers learn about problems early when interventions remain simple and inexpensive rather than after issues escalate.
Planned Disruption Communication
Advance notice about maintenance activities minimizes inconvenience:
- Schedules for activities affecting classrooms, technology, or building access
- Alternative arrangements during disruptions (temporary locations, modified schedules)
- Expected duration and completion estimates
- Contact information for questions or problems
- Updates when schedules change or unexpected issues arise
Proactive communication transforms maintenance activities from surprising disruptions into expected, planned events that stakeholders can prepare for and work around.
Community and Public Communication
External stakeholders deserve transparency about facility conditions and improvement planning:
Facility Condition Reporting
Regular reporting demonstrates stewardship while supporting bond issue campaigns:
- Annual facility condition reports summarizing assessments and improvement needs
- Multi-year capital improvement plans showing investment strategies
- Project completion updates celebrating improvements and responsible management
- Budget allocation transparency showing facility spending priorities
- Comparison data demonstrating efficiency and value relative to peers
Transparent facility reporting builds community trust while establishing credibility supporting requests for improvement funding through bonds or operating budget increases.
Community Input Processes
Engaging community members in facility planning builds support and incorporates diverse perspectives:
- Surveys gathering input on priorities and preferences
- Community forums discussing facility needs and improvement options
- Building tours showing conditions and explaining maintenance challenges
- Planning committee participation including diverse community representatives
- Feedback on proposed projects before final decisions
Community engagement transforms facility management from invisible technical work into collaborative stewardship where stakeholders understand challenges, contribute to solutions, and support necessary investments.

Interactive displays and welcoming facilities support community engagement while demonstrating institutional commitment to excellence and recognition
Professional Development and Staff Training
Facilities management effectiveness depends on knowledgeable, skilled staff maintaining expertise as building systems and best practices evolve.
Ongoing Technical Training
Continuous learning ensures staff maintain capabilities with modern systems:
Equipment-Specific Training
As buildings incorporate advanced systems, staff need specialized knowledge:
- HVAC controls and building automation systems operation and troubleshooting
- Modern lighting systems and control technology
- Security systems and access control management
- Technology infrastructure and network systems
- Energy management systems and optimization strategies
Manufacturer-provided training, professional association workshops, and technical college partnerships provide training options ensuring staff capabilities match building system sophistication.
Safety and Compliance Training
Regulatory requirements and safety protocols require regular training:
- OSHA safety standards and hazard communication
- Bloodborne pathogen exposure prevention
- Confined space entry procedures
- Ladder and lift safety protocols
- Chemical handling and storage requirements
- Emergency response procedures and roles
Regular safety training protects staff while ensuring regulatory compliance that protects institutions from liability and citations.
Leadership and Professional Development
Beyond technical skills, facilities management requires leadership and strategic capabilities:
Professional Association Participation
Organizations like APPA (formerly the Association of Physical Plant Administrators) provide resources supporting professional growth:
- Annual conferences featuring industry best practices and emerging trends
- Certification programs validating facilities management competencies
- Peer networking enabling knowledge sharing and problem-solving
- Research and publications documenting effective practices
- Advocacy for adequate facilities funding and policy development
Professional development investments yield returns through improved effectiveness, reduced turnover, and enhanced credibility supporting budget requests and strategic initiatives.
Conclusion: Strategic Facilities Management Advancing Educational Excellence
Effective school facilities management has evolved far beyond basic maintenance and cleaning into strategic organizational functions directly supporting educational mission achievement. The comprehensive approaches explored in this guide—from preventive maintenance systems and technology integration through sustainability initiatives and recognition-rich environments—transform buildings from simple containers for education into active contributors supporting student learning, teacher effectiveness, and community pride.
Modern facilities directors must balance competing priorities: maintaining aging infrastructure with limited budgets, integrating advancing technology supporting contemporary pedagogy, implementing sustainability practices demonstrating environmental stewardship, and creating welcoming environments celebrating achievement while supporting diverse learning needs. Success requires systematic approaches replacing reactive crisis management with proactive planning, data-driven decision-making, and stakeholder engagement ensuring facility investments align with educational priorities.
Transform Your School Facilities with Modern Recognition Displays
Discover how digital recognition solutions enhance school environments while celebrating achievement and building community pride as part of comprehensive facility improvement initiatives.
Explore Recognition SolutionsThe strategies presented provide actionable frameworks applicable across different building types, district sizes, and resource levels. From implementing CMMS platforms streamlining operations to installing digital recognition displays celebrating achievement, each initiative contributes to environments supporting educational excellence while demonstrating responsible stewardship of community resources.
Begin where you are with improvements delivering immediate impact—perhaps systematic preventive maintenance reducing crisis repairs, energy efficiency projects generating budget relief, or recognition display installations showcasing institutional pride. Then systematically expand toward comprehensive facilities management programs your students, staff, and community deserve.
Every well-maintained building, every recognition display celebrating achievement, every sustainability initiative demonstrating environmental commitment—these represent visible manifestations of institutional values and educational priorities. With strategic planning, systematic execution, and continuous improvement, facilities management transforms from necessary operational expense into strategic investment advancing educational excellence while building community pride in shared institutional assets.
Your school community deserves environments that inspire learning, celebrate achievement, and demonstrate commitment to excellence. Through thoughtful facilities management incorporating preventive maintenance, technology integration, recognition displays, and stakeholder engagement, you can create spaces where every aspect of the physical environment supports educational success and community pride. Explore resources on staff appreciation and recognition, discover elementary school recognition solutions, and learn about digital signage content strategies that enhance facility communication while building community engagement with institutional excellence.