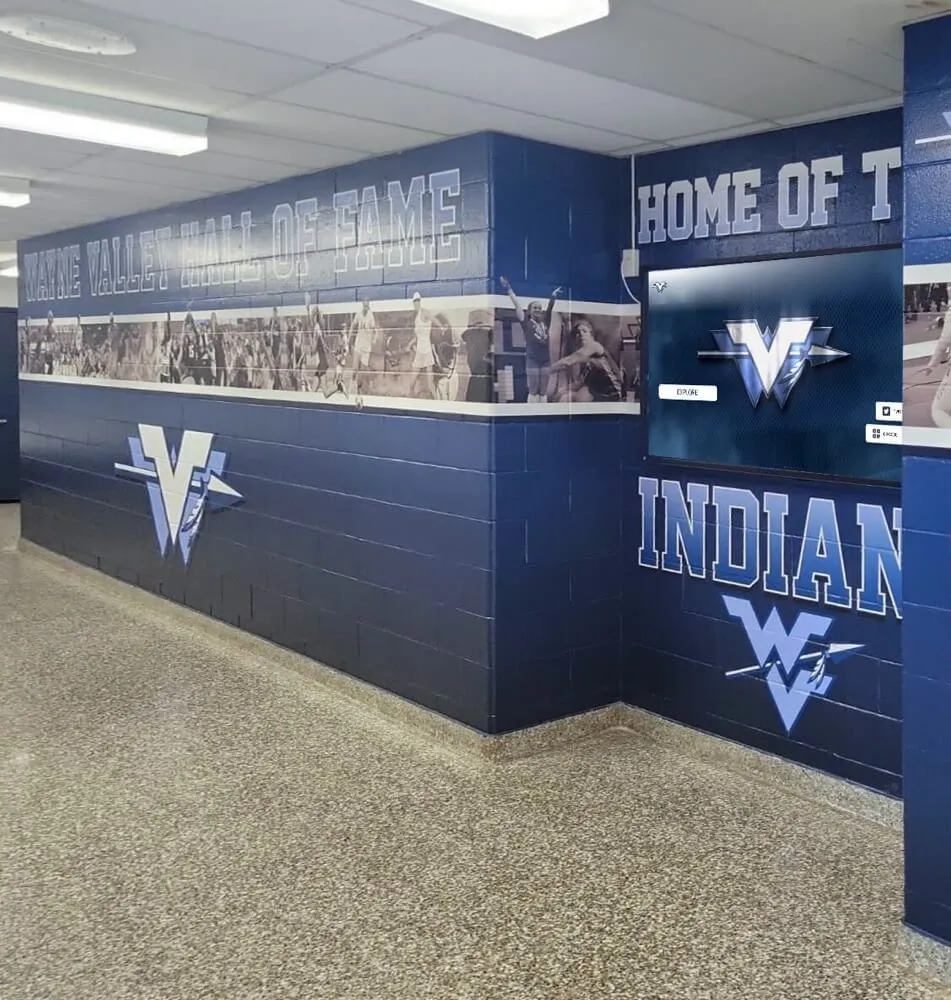
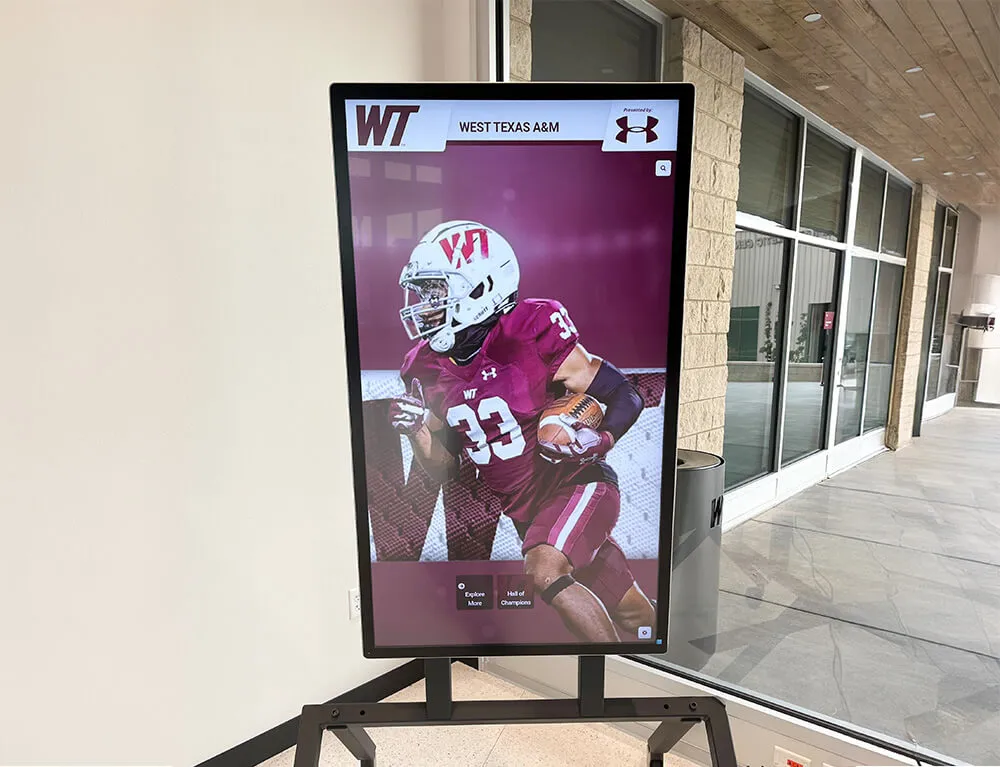
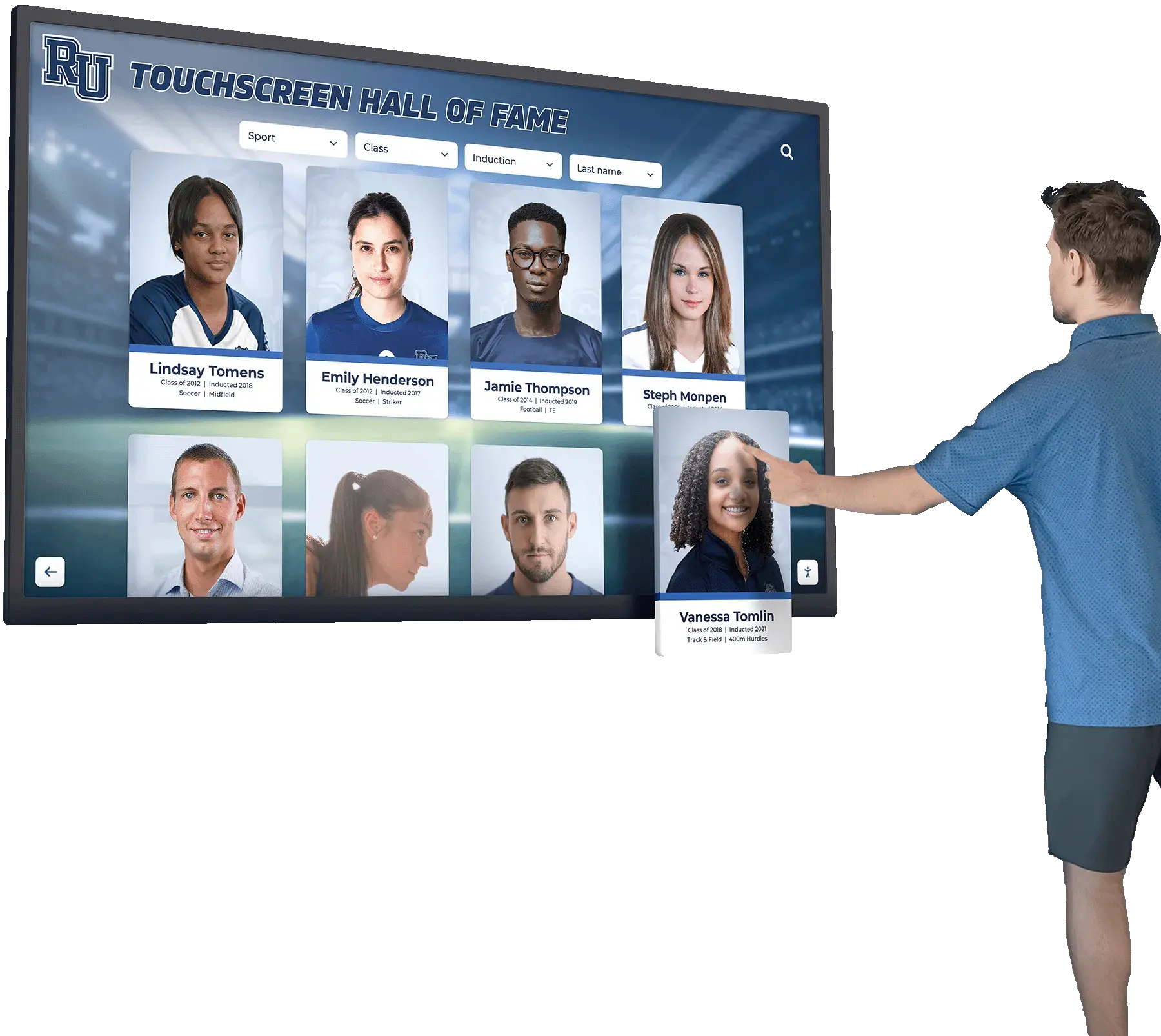
Senior mentors represent some of the most valuable yet often underrecognized contributors to school communities—accomplished upper-class students who dedicate time and energy to guiding younger peers through academic challenges, social transitions, and personal development. These student leaders bridge gaps that even exceptional faculty cannot fully address, offering relatable perspectives, peer credibility, and empathetic understanding rooted in recent shared experiences.
Yet despite the profound impact that senior mentors create, many schools struggle to provide recognition commensurate with their contributions. Mentorship often happens quietly behind the scenes without the public visibility that athletic achievements or academic honors routinely receive. Senior mentors graduate without adequate celebration of their service, younger students miss inspiring examples of peer leadership they might emulate, and schools lose opportunities to demonstrate the comprehensive leadership development they foster beyond traditional extracurricular activities.
This comprehensive guide explores proven strategies for recognizing and celebrating senior student mentors in ways that honor their contributions, inspire future generations of peer leaders, demonstrate institutional commitment to student-centered support, and create lasting documentation of mentorship’s transformative impact on school communities.
Senior mentor recognition serves multiple strategic purposes beyond simple acknowledgment. Effective programs strengthen recruitment of future mentors by showcasing the honor and respect that mentorship earns, validate the time commitment and emotional investment mentors make supporting peers, inspire younger students to aspire toward leadership roles serving their communities, demonstrate to families and stakeholders that schools value peer support and student leadership, create institutional memory preserving the legacy of students who shaped school culture through service, and provide mentors with documented leadership experiences valuable for college applications and career opportunities.

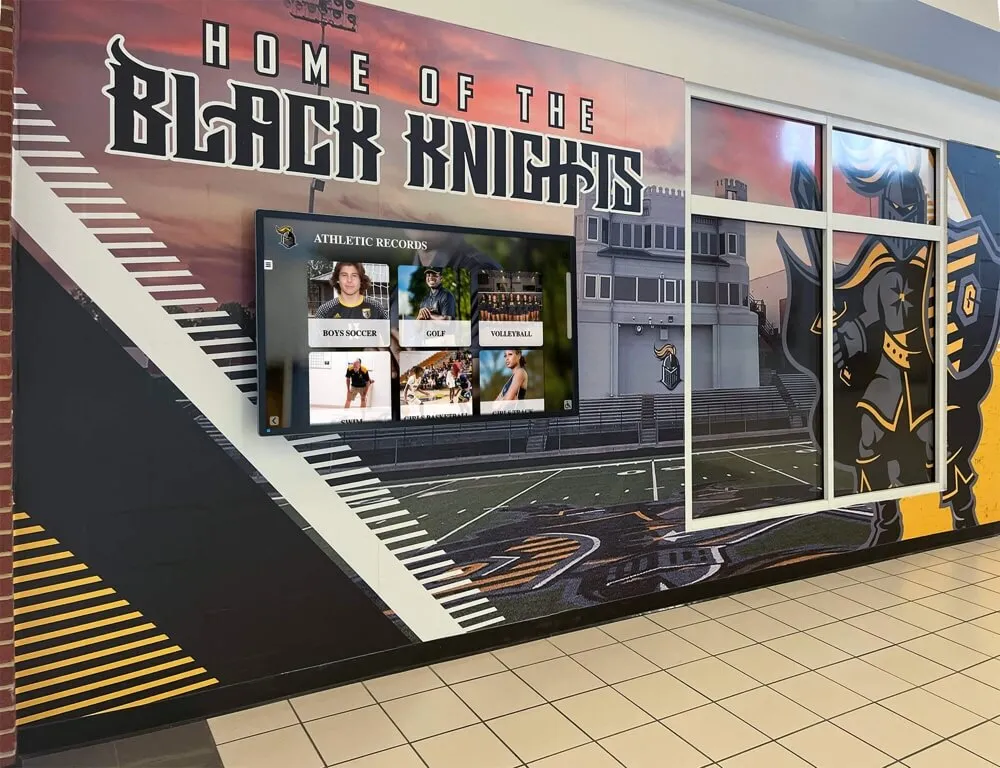
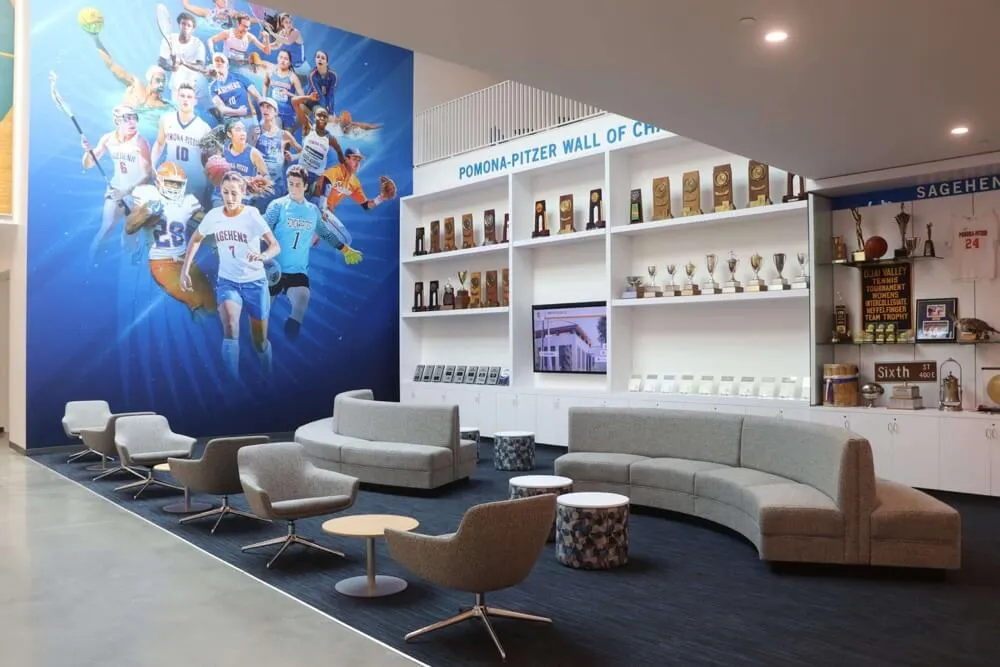
Modern recognition displays enable community members to explore senior mentor contributions and leadership journeys through engaging interactive interfaces
Understanding Senior Mentorship Programs in Educational Settings
Before developing recognition strategies, understanding the diverse forms that senior mentorship takes across educational institutions helps schools create acknowledgment approaches that authentically reflect program structures and mentor contributions.
Types of Peer Mentorship Models
Senior mentorship programs vary significantly across institutions based on educational philosophy, student populations, and available resources:
Academic Peer Tutoring and Support
Many schools implement structured programs where high-achieving seniors provide academic assistance to younger students struggling with coursework. These mentors typically focus on specific subjects where they have demonstrated mastery, offering homework help during study halls, tutoring sessions after school, or embedded support within classrooms. Academic mentorship proves particularly valuable in STEM subjects where students commonly hit conceptual walls requiring peer explanation that often resonates more effectively than teacher instruction.
According to research from the National Mentoring Resource Center, school-based mentoring programs that include academic support components show significant positive effects on student academic performance and engagement. Students receiving peer academic mentorship demonstrate improved grades, higher homework completion rates, and increased confidence in challenging subjects.
Transition and Orientation Mentorship
Senior mentors frequently guide incoming students through challenging transitions into new school environments. High school seniors support incoming freshmen navigating complex campus layouts, understanding academic expectations, managing increased workload, decoding social dynamics, and developing organizational systems essential for success. College seniors similarly support first-year students adjusting to residential life, increased academic independence, and adult responsibilities.
These transition mentorship programs typically concentrate efforts during summer orientation, the first weeks of school, and critical junctures throughout the first year when adjustment challenges commonly emerge. The mentorship provides emotional support and practical guidance that helps prevent the isolation and overwhelm that drives early academic struggles and dropout risk.

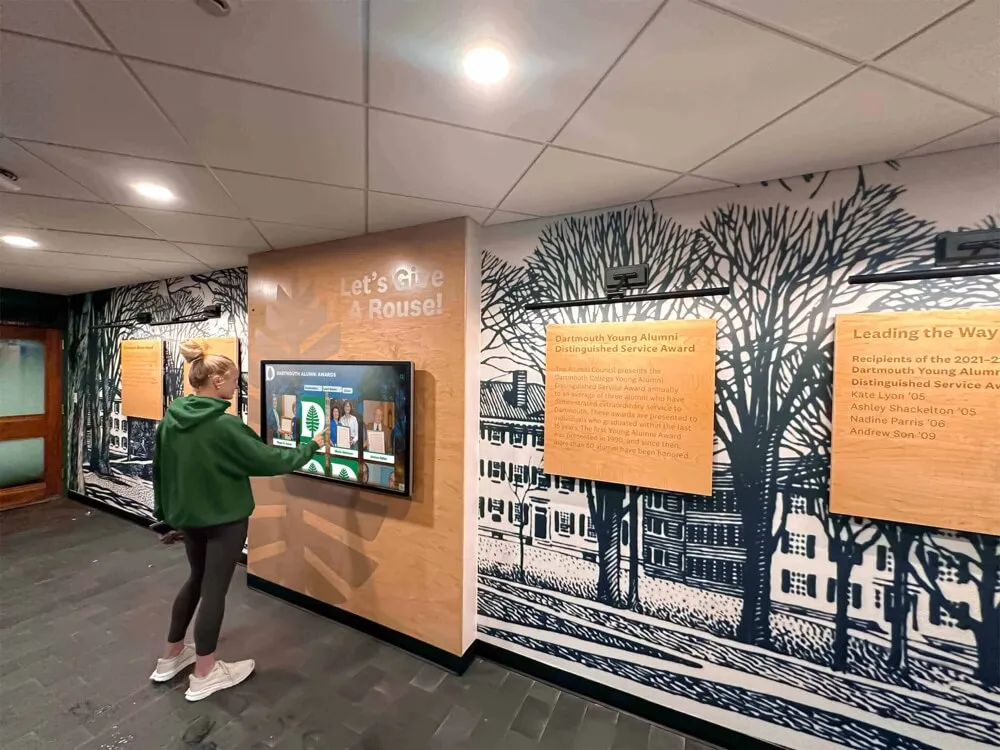
Recognition displays showcasing senior mentor achievements inspire younger students while demonstrating the lasting impact of peer leadership service
Social-Emotional and Wellness Mentorship
Many schools train senior students to provide social-emotional support addressing mental health, stress management, relationship challenges, and personal development. These mentors receive specialized training in active listening, resource referral, crisis recognition, and supportive communication. They complement professional counseling services by offering accessible peer support students often feel more comfortable approaching than adult professionals.
Wellness mentorship gained significant prominence following the mental health challenges that intensified during 2020-2021. Schools increasingly recognize that peer support networks complement professional services while normalizing help-seeking and reducing stigma around mental health struggles.
Leadership Development and Life Skills Mentorship
Some mentorship programs focus on cultivating leadership capabilities in younger students through senior mentor modeling and guidance. These programs teach goal-setting, decision-making, time management, conflict resolution, and other life skills essential for success. Senior mentors share their own leadership journeys, provide accountability for mentee goals, and create safe spaces for younger students to develop confidence and self-efficacy.
Leadership mentorship often targets specific student populations including first-generation college students, students from underrepresented backgrounds, or those showing leadership potential who would benefit from individualized development support. Learn more about comprehensive approaches to student mentorship alumni discovery programs that connect current students with successful graduates.
Identity-Based and Affinity Mentorship
Many institutions create mentorship programs connecting seniors and younger students who share common identities, experiences, or interests. These affinity-based programs might focus on cultural heritage, gender identity, athletic participation, academic interests, or other dimensions where shared experience creates powerful connection and understanding.
Identity-based mentorship proves particularly valuable for students from marginalized communities who benefit from seeing successful peers who share aspects of their identity and have navigated similar challenges. Senior mentors provide representation, validate experiences, and demonstrate that success is achievable despite obstacles specific communities face.
The Unique Value Senior Mentors Provide
Understanding what makes peer mentorship uniquely effective helps schools appreciate why recognition matters:
Credibility Through Shared Experience
Senior mentors possess credibility that adult educators, regardless of skill or dedication, cannot fully replicate. They have recently experienced the exact challenges their mentees face—the specific teachers, course requirements, social dynamics, and institutional culture that shape student experience. This recent navigation of the same terrain makes their guidance immediately relevant and actionable.
When a senior mentor says “I struggled with that too, here’s what worked for me,” younger students hear practical wisdom from someone who genuinely understands their situation rather than abstract advice from adults whose high school experience occurred decades earlier in vastly different contexts.
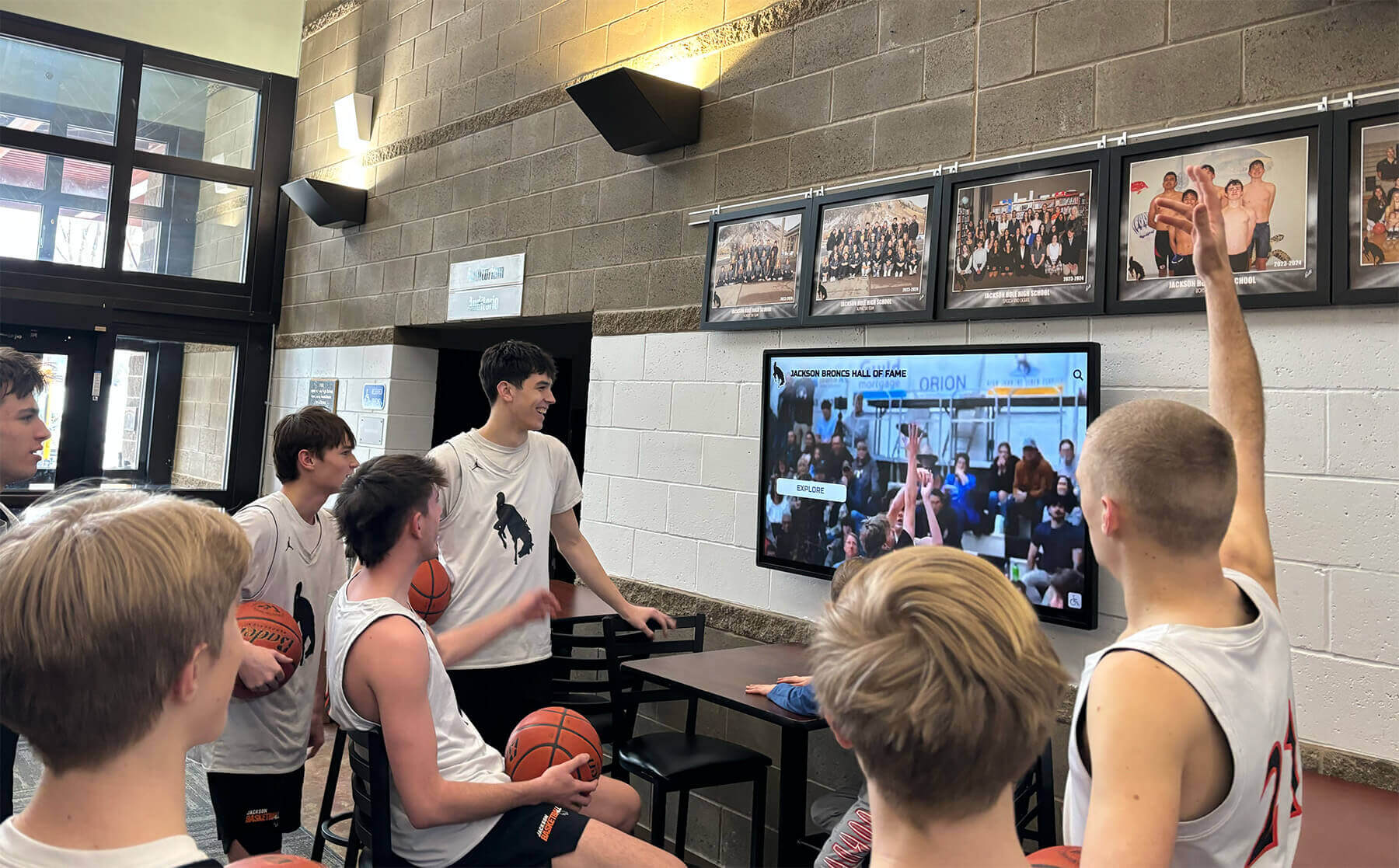

Group engagement with recognition displays creates natural discussions about leadership pathways and mentorship opportunities among students
Reduced Power Differential and Approachability
The hierarchical relationship between students and teachers, while professionally appropriate, creates barriers that prevent some students from seeking help or sharing struggles. Senior mentors occupy a different relational space—they are fellow students, slightly further along the journey, without formal authority that might intimidate younger peers.
Many students who would never visit a teacher’s office hours or approach a school counselor feel comfortable texting a senior mentor, catching them in the hallway, or joining a casual mentorship gathering. This approachability proves essential for reaching students who most need support but hesitate to access formal adult services.
Modeling Attainable Success
When younger students see teachers, administrators, or successful adults in the community, the developmental and experiential gap can make those successes feel abstract or unattainable. Senior mentors provide tangible, proximate models of success that younger students can realistically imagine achieving.
A freshman struggling academically can look at their senior mentor—who perhaps struggled similarly in their freshman year before developing effective study systems—and think “if they could figure this out, so can I.” This proximate modeling creates self-efficacy that distant role models, however accomplished, often cannot inspire.
Cultural Knowledge Transfer
Every school possesses unwritten rules, insider knowledge, and cultural nuances that significantly impact student success but rarely appear in handbooks or orientation materials. Senior mentors transmit this essential cultural knowledge: which teachers appreciate which communication styles, how to navigate complex social situations, where to find quiet study spaces, how to access hidden resources, and countless other insights that distinguish insiders from outsiders.
This cultural transmission particularly benefits first-generation students, transfer students, and others without family members who can provide insider guidance about navigating educational institutions successfully. Explore how Big Brother Big Sister programs create similar mentorship relationships across broader community contexts.
The Developmental Benefits Mentors Gain from Service
While recognition often focuses on benefits mentorship provides mentees, understanding what senior mentors gain from service helps schools communicate value to potential mentors and design recognition that acknowledges their growth.
Leadership Skill Development
Mentorship forces seniors to develop sophisticated leadership capabilities essential for future success:
Communication and Active Listening
Effective mentoring requires seniors to practice clear communication adapted to different learning styles and maturity levels. They learn to explain complex concepts accessibly, ask probing questions revealing underlying issues, provide constructive feedback without discouragement, and listen actively to understand rather than simply respond.
These communication skills translate directly to professional contexts where the ability to teach, influence, and support colleagues determines career success and leadership effectiveness.
Emotional Intelligence and Empathy
Working with younger students navigating challenges develops mentors’ emotional intelligence. They practice recognizing others’ emotional states through verbal and non-verbal cues, responding with empathy and appropriate support, managing their own emotional responses to others’ struggles, setting appropriate boundaries in helping relationships, and recognizing when situations require professional intervention beyond peer support capacity.
Research from the Association for Psychological Science demonstrates that mentoring relationships enhance emotional intelligence and perspective-taking abilities in mentors themselves, not just mentees—benefits that extend throughout mentors’ personal and professional lives.

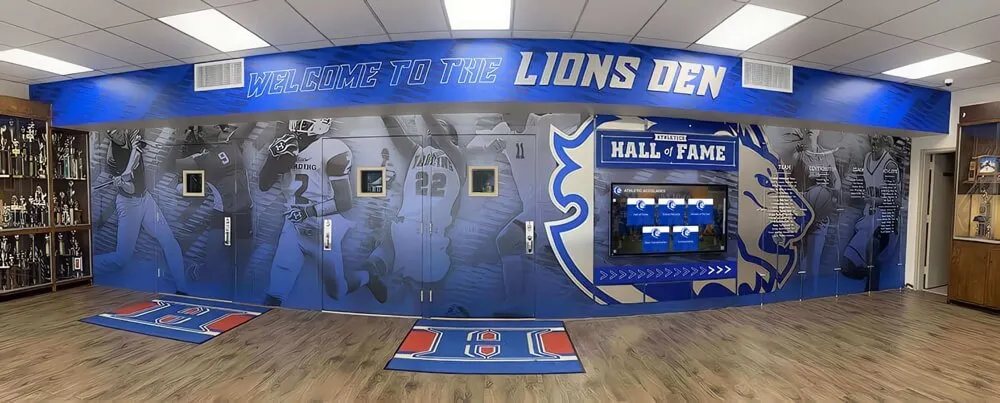
Individual recognition profiles celebrate specific mentorship contributions and leadership development journeys across academic careers
Problem-Solving and Adaptability
Mentorship presents continuously evolving challenges requiring flexible problem-solving. Mentors must assess unique situations without predetermined solutions, adapt approaches when initial strategies prove ineffective, manage ambiguity and incomplete information, balance multiple competing priorities, and recognize when to seek guidance from program advisors.
These problem-solving experiences provide invaluable preparation for professional environments characterized by complexity, ambiguity, and the need for independent judgment under uncertain conditions.
Personal Growth and Self-Understanding
Beyond skill development, mentorship catalyzes profound personal growth:
Enhanced Self-Awareness
Explaining study strategies, time management systems, or life approaches to mentees forces mentors to articulate and examine their own practices. This reflection commonly reveals both strengths worth cultivating and limitations worth addressing. Many senior mentors report that mentorship taught them more about themselves than any formal course or activity.
Purpose and Contribution
Adolescence and early adulthood often involve searching for meaning and purpose beyond individual achievement. Mentorship provides concrete opportunities to contribute meaningfully to others’ lives and school communities. Senior mentors consistently cite the profound satisfaction of knowing they made genuine difference for younger students navigating challenges they understand intimately.
Perspective and Gratitude
Supporting students facing significant challenges often helps mentors develop perspective on their own difficulties and gratitude for resources they may have previously taken for granted. Mentors from privileged backgrounds particularly benefit from exposure to peers managing obstacles they never faced, developing empathy and understanding essential for effective leadership in diverse communities.
Resume and Application Enhancement
Pragmatically, documented mentorship leadership provides substantial value for college and career applications:
Demonstrated Leadership and Service
Competitive colleges and selective employers seek evidence of leadership, service commitment, and positive community impact. Sustained mentorship involvement—particularly with documentation of specific contributions, challenges overcome, and outcomes achieved—provides concrete evidence distinguishing applicants from peers with comparable academic credentials.
Compelling Application Narratives
Mentorship experiences generate authentic, compelling stories for application essays and interviews. Rather than generic statements about leadership aspirations, mentors can share specific moments when they helped a struggling freshman succeed academically, supported a mentee through personal crisis, or adapted their approach after initial strategies failed. These concrete narratives resonate powerfully with admissions officers and hiring managers.
Professional References and Recommendations
Faculty advisors supervising mentorship programs can provide detailed, substantive recommendation letters describing observable leadership development and specific positive impacts. These letters carry more weight than generic recommendations because they describe concrete behaviors and documented outcomes rather than abstract character assessments.
Learn about comprehensive approaches to academic recognition programs that celebrate diverse student achievements including leadership and service contributions.
Designing Comprehensive Senior Mentor Recognition Programs
Effective recognition requires thoughtful program design addressing multiple dimensions of acknowledgment and celebration.
Multi-Tiered Recognition Structures
Different recognition levels ensure appropriate acknowledgment across varying commitment and impact levels:
Daily and Weekly Acknowledgment
Frequent small recognition maintains mentor motivation and ensures consistent visibility:
- Morning announcements highlighting individual mentor contributions and success stories
- Social media posts celebrating mentor-mentee pairs and program milestones
- Digital displays featuring rotating mentor profiles throughout common areas
- Classroom shout-outs when teachers observe mentors supporting peers
- Hallway displays with “Mentor of the Week” features and photos
Monthly and Quarterly Recognition
Regular recognition ceremonies create anticipated celebration touchpoints:
- Monthly mentor appreciation events with light refreshments and peer connection
- Quarterly recognition assemblies honoring mentorship achievements
- Mentor spotlight features in school newsletters and communications
- Subject-specific mentor awards acknowledging specialized contributions
- Recognition at school board meetings demonstrating institutional value for mentorship
Annual and Graduation Recognition
Culminating celebrations honor sustained commitment and program completion:
- Year-end mentor appreciation dinners or recognition ceremonies
- Senior graduation recognition specifically acknowledging mentorship service
- Permanent recognition in yearbooks, legacy displays, and school archives
- Formal certificates, letters, or awards documenting mentorship leadership
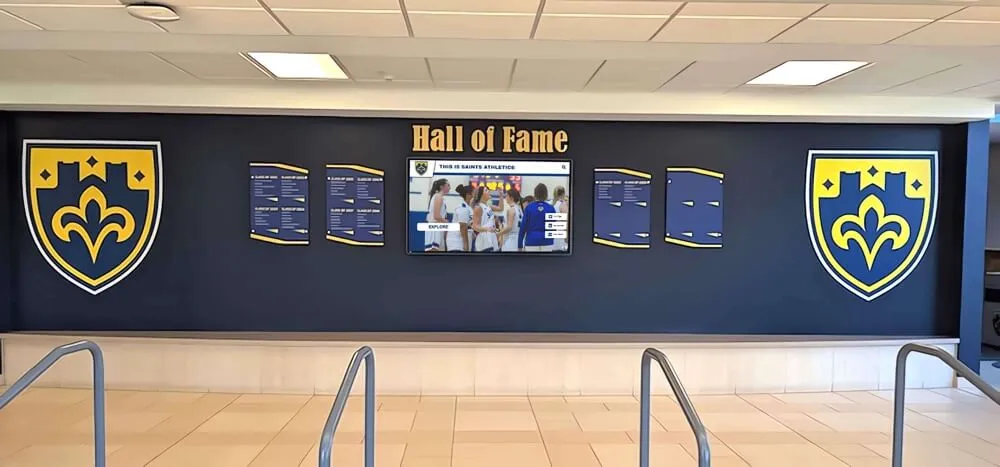
- Induction into mentorship halls of honor for multi-year participants
This tiered structure ensures recognition feels continuous and meaningful throughout mentorship involvement while building toward significant graduation acknowledgment. Explore senior recognition program strategies that honor sustained contributions to school communities.

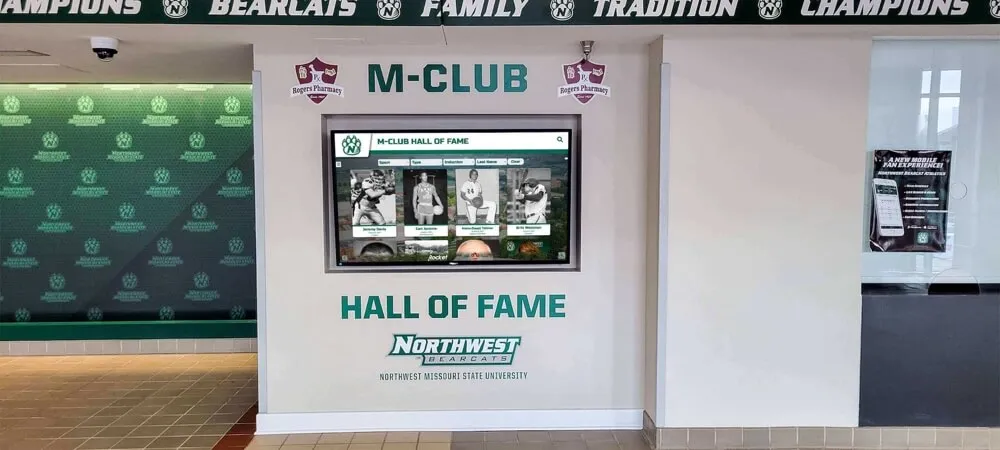
Digital recognition platforms enable schools to showcase diverse student leaders including mentors, athletes, and academic achievers in unified systems
Traditional Recognition Formats
Conventional approaches provide tangible acknowledgment many stakeholders value:
Physical Recognition Displays
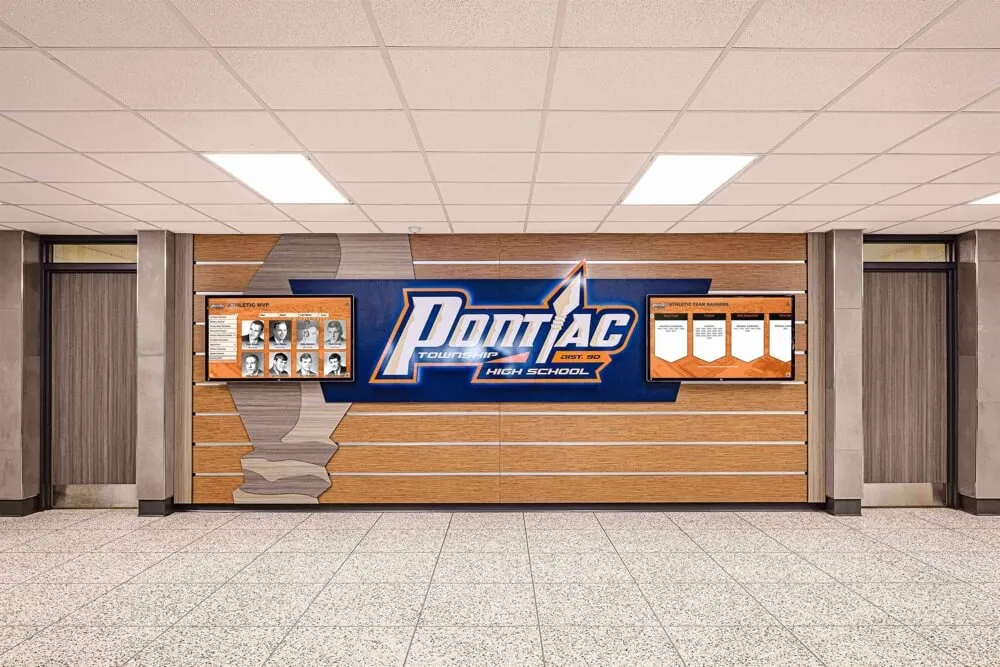
Visible recognition throughout school buildings demonstrates institutional commitment:
- Dedicated mentor recognition walls with photos and brief biographical profiles
- Trophy cases or display areas housing mentorship program awards and memorabilia
- Hallway bulletin boards featuring current mentor cohorts and their achievements
- Library or student center displays highlighting mentorship program history
- Classroom recognitions for subject-specific academic mentors
These physical displays ensure that mentorship receives visibility comparable to athletic achievements or academic honors, communicating that schools value leadership and service equally to traditional accomplishments.
Certificates and Awards
Formal documentation provides mentors with tangible recognition useful for applications:
- Completion certificates for mentorship program participation
- Service hour documentation letters for scholarship and college applications
- Leadership awards recognizing exceptional mentor contributions
- Subject-specific recognition for academic mentoring excellence
- Character awards honoring mentors’ integrity, empathy, and dedication
Ceremonial Recognition
Special events create memorable celebration experiences:
- Senior awards nights featuring mentorship recognition categories
- Graduation ceremony acknowledgment of mentorship service
- Mentorship program induction ceremonies for new participants
- Year-end banquets honoring mentor achievements and contributions
- Pinning ceremonies providing symbolic mentorship designation recognition
These ceremonies provide important rites of passage marking mentorship as significant accomplishment worthy of formal celebration. Learn about teacher of the year award recognition approaches that can inform mentor acknowledgment strategies.
Modern Digital Recognition Solutions
Contemporary technology transforms recognition possibilities while overcoming traditional format limitations:
Interactive Digital Displays
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built platforms transforming mentor recognition through unlimited capacity accommodating every mentor across program history, searchable databases enabling visitors to find specific mentors or browse by categories, multimedia content incorporating photos, videos, and detailed biographical narratives, automatic updates allowing instant content additions without construction or manufacturing, and dynamic presentation rotating featured content preventing static appearance.
Digital systems particularly benefit schools with large mentorship programs where physical space limitations prevent comprehensive traditional recognition. Every mentor receives equal recognition capacity regardless of when they participated or how many mentors came before or after them.
Online Recognition Portals
Web-accessible platforms extend recognition beyond physical campus:
- Dedicated mentorship program website sections featuring all current and historical mentors
- Searchable mentor directories organized by graduation year, mentorship focus, and achievement type
- Featured mentor stories with extended narratives and multimedia content
- Social sharing capabilities enabling mentors to showcase recognition in personal networks
- Alumni connections linking current mentors with program graduates who became successful professionals
Online recognition ensures families, community members, and college admissions officers can discover mentor achievements regardless of geographic location or campus visiting ability.
Social Media Recognition Campaigns
Strategic social media use amplifies recognition reach and creates ongoing engagement:
- Regular mentor spotlight posts featuring individual contributions and stories
- Mentorship Monday series creating predictable weekly recognition
- Mentor-mentee pair features celebrating successful relationships
- Video testimonials from mentees describing how mentors impacted their lives
- Behind-the-scenes content showing mentorship program activities and training
Social media’s viral potential enables recognition to reach far beyond immediate school community, raising program profile while providing mentors with shareable content demonstrating their leadership.
Mobile Applications and Digital Badges
Emerging technologies create portable recognition mentors can carry:
- Digital badges mentors can display on LinkedIn profiles and digital portfolios
- Mobile apps providing centralized access to mentorship achievements and documentation
- QR codes on badges or credentials linking to detailed mentor profiles
- Blockchain-verified credentials providing tamper-proof documentation for applications
- Integration with e-portfolio systems students use for comprehensive achievement tracking
These digital credentials ensure recognition remains accessible and verifiable long after graduation when mentors need documentation for career opportunities. Discover how digital recognition displays transform traditional approaches to celebrating achievements.
Implementing Mentor Recognition Into Existing Program Structures
Recognition proves most effective when integrated systematically throughout mentorship programs rather than added as afterthought.
Recognition-Integrated Program Design
Building recognition into program foundations ensures consistency and sustainability:
Mentorship Application and Selection Recognition
Begin recognition at program entry through selective application processes communicating that mentorship represents honor, competitive selection acknowledging that not all applicants may be chosen, acceptance ceremonies welcoming new mentors into program community, public announcements celebrating new mentor cohorts, and orientation materials emphasizing the prestigious tradition mentors join.
This early recognition frames mentorship as achievement worth pursuing rather than casual volunteer opportunity requiring no particular qualification or commitment.
Training and Development Recognition
Acknowledge mentor skill development throughout preparation:
- Certificates for completing mentorship training modules
- Recognition at training completion ceremonies
- Digital badges for specialized skill certifications
- Public acknowledgment of mentors pursuing advanced training
- Featured profiles of mentors demonstrating exemplary program knowledge
Training recognition validates the significant learning investment mentorship requires while motivating thorough engagement with preparation materials and skill development opportunities.

Accessible campus displays enable students to explore mentorship opportunities and discover senior leader profiles during regular school activities
Ongoing Performance Recognition
Systematic acknowledgment throughout service maintains motivation and excellence:
- Monthly recognition for mentors demonstrating exceptional commitment or achieving milestones
- Peer-nominated awards where mentors recognize colleagues’ outstanding contributions
- Mentee feedback systems informing recognition of particularly effective mentors
- Improvement recognition for mentors developing skills and expanding capabilities
- Consistency awards honoring mentors maintaining regular engagement throughout term
Performance recognition should emphasize effort, growth, and commitment rather than exclusively rewarding natural talent, ensuring all dedicated mentors receive acknowledgment regardless of initial skill levels.
Transition and Alumni Recognition
Continue recognition beyond active service creating lasting connection:
- Graduation recognition specifically highlighting mentorship contributions
- Alumni mentor networks maintaining relationships among program graduates
- Career milestone acknowledgment as mentor alumni achieve professional success
- Mentor alumni spotlights in program communications and recognition displays
- Legacy recognition when mentor alumni send their own children through schools where they served
This long-term recognition communicates that mentorship creates lifelong identity and connection rather than temporary student activity forgotten after graduation. Learn about alumni recognition wall strategies that maintain connections across generations.
Cross-Functional Integration
Maximize recognition impact by connecting with existing school systems:
Academic Integration
Link mentorship recognition to academic structures and incentives:
- Course credit for mentorship participation increasing transcript value
- Honor society membership consideration including mentorship service
- Academic award ceremonies incorporating mentorship recognition categories
- Graduation honors calculations crediting leadership and service activities
- Transcript notations documenting mentorship involvement and achievements
Academic integration ensures mentorship receives recognition comparable to classroom achievements while providing practical application benefits.
Extracurricular Coordination
Coordinate mentorship recognition with broader student activities:
- Student government positions for mentorship program leadership
- Club fair representation showcasing mentorship as valuable activity option
- Homecoming and school spirit events featuring mentor recognition components
- Yearbook sections documenting mentorship program and participants
- Award banquet inclusion alongside athletic and artistic recognition
This coordination prevents mentorship from existing in isolation, instead positioning it as central element of comprehensive student leadership development.
Community Partnership Integration
Extend recognition through external community connections:
- Local business sponsorship of mentor recognition awards and events
- Civic organization presentations highlighting school mentorship programs
- Media coverage celebrating mentor achievements and program impact
- Scholarship opportunities specifically for students demonstrating mentorship leadership
- Career networking events connecting mentors with community professionals
Community integration demonstrates mentorship value beyond school walls while providing mentors with expanded opportunities and recognition. Explore corporate sponsorship recognition approaches applicable to mentorship programs.
Best Practices for Meaningful Mentor Recognition
Effective recognition requires attention to what makes acknowledgment feel genuine and valuable rather than perfunctory or generic.
Personalization and Authenticity
Generic recognition often feels hollow—meaningful acknowledgment requires personal touches:
Specific Contribution Recognition
Rather than vague praise, acknowledge concrete contributions:
- Detailed descriptions of specific mentees helped and challenges addressed
- Documentation of particular skills, strategies, or approaches mentors developed
- Recognition of challenging situations mentors navigated successfully
- Acknowledgment of growth areas where mentors improved throughout program
- Celebration of unique contributions reflecting individual mentor strengths
This specificity demonstrates that recognition comes from genuine awareness and appreciation rather than obligatory acknowledgment.
Personal Narrative Inclusion
Effective recognition tells mentors’ individual stories:
- Background information about what motivated mentors to serve
- Journey narratives describing mentors’ development throughout involvement
- Challenges overcome during mentorship experience
- Personal reflections from mentors about what they learned
- Future plans and how mentorship preparation connects to aspirations
Story-based recognition creates emotional resonance while providing compelling examples inspiring future potential mentors. Discover digital storytelling approaches that bring recognition to life.
Mentee Voice Integration
The most powerful recognition often comes from those mentors served:
- Written testimonials from mentees describing mentor impact
- Video messages from mentees sharing gratitude and specific examples
- Letters from mentees included in mentor recognition portfolios
- Joint mentor-mentee recognition celebrating successful relationships
- Mentee-led recognition events or presentations honoring their mentors
These mentee perspectives provide authentic validation that no amount of adult praise can match, offering mentors concrete evidence of difference they made.
Equity and Inclusion in Recognition
Recognition systems must avoid inadvertently favoring certain mentor types over others:
Multiple Excellence Pathways
Diverse recognition categories ensure varied strengths receive acknowledgment:
- Consistency awards for reliable, steady engagement
- Innovation recognition for creative mentorship approaches
- Empathy awards honoring exceptional emotional support
- Challenge navigation recognition for overcoming program obstacles
- Growth awards celebrating significant skill development
- Collaboration recognition for outstanding teamwork and peer support

Comprehensive recognition systems document leadership contributions across multiple years and create lasting institutional legacy
Peer Nomination Opportunities
Fellow mentors often notice contributions adults miss:
- Peer recognition awards where mentors nominate colleagues
- Anonymous appreciation systems enabling mentors to acknowledge each other
- Peer-voted recognition categories in addition to advisor-selected awards
- Spotlight opportunities showcasing mentors recommended by peers
- Collaborative recognition celebrating effective mentor teams
Peer acknowledgment carries unique weight because it comes from those who truly understand mentorship demands and can assess quality from experience.
Addressing Access and Opportunity Barriers
Ensure recognition doesn’t create financial or social barriers:
- No-cost recognition events and materials accessible to all mentors
- Multiple recognition formats accommodating different preferences and schedules
- Virtual options for mentors unable to attend in-person events
- Translation services for mentors from multilingual communities
- Accessibility accommodations for mentors with disabilities
Inclusive recognition design ensures every mentor can fully participate regardless of personal circumstances or resources.
Measuring and Communicating Recognition Impact
Systematic assessment demonstrates recognition value while informing continuous improvement.
Recognition Effectiveness Metrics
Quantitative measures reveal program success and areas for enhancement:
Participation and Retention Indicators
Track how recognition affects mentor engagement through application rates for mentorship programs year-over-year, retention rates of mentors continuing through program completion, mentor satisfaction surveys assessing recognition adequacy, competitive ratios showing how many students apply versus openings available, and returning mentor percentages indicating likelihood of multi-year involvement.
Positive trends suggest recognition effectively supports recruitment and retention while negative patterns reveal opportunities for improvement.
Recognition Distribution Analysis
Ensure equitable recognition across mentor populations through demographic breakdown of recognition recipients, subject or focus area representation in recognition, grade level distribution among recognized mentors, recognition frequency analysis preventing over-acknowledgment of some at expense of others, and proportional representation analysis comparing mentor demographics to recognition recipients.
Systematic equity monitoring prevents recognition from inadvertently favoring mentors who already enjoy other advantages while missing equally deserving peers from different backgrounds or mentorship focus areas.
Impact Documentation
Measure recognition effects on desired outcomes including mentor skill development self-assessment before and after recognition, college application inclusion rates showing how many mentors document experience, employment and internship success rates for program alumni, alumni engagement indicating mentor alumni continuing school connections, and community perception surveys assessing how recognition affects institutional reputation.
These impact measures justify recognition investment while revealing long-term benefits extending beyond immediate program operations. Learn about measuring engagement and recognition effectiveness through comprehensive analytics.
Success Story Documentation
Qualitative evidence provides compelling recognition impact demonstration:
Mentor Testimonials
Systematic collection of mentor voices builds powerful evidence:
- Written reflections from graduating mentors about recognition meaning
- Video interviews capturing mentors discussing recognition value
- Exit surveys gathering feedback on recognition program effectiveness
- Alumni follow-up documenting how recognition influenced future opportunities
- Parent perspectives on how recognition affected their children’s development
These personal accounts humanize recognition impact while providing content for marketing and fundraising supporting continued program investment.
Mentee Impact Narratives
Document how recognition affects mentees and program outcomes:
- Mentee testimonials describing how mentor recognition motivated their own aspirations
- Younger student reflections on how visible recognition inspired them to pursue mentorship
- Academic and social outcome data for students served by recognized mentors
- School climate data showing how recognition affects overall culture
- Community partner observations about program credibility and reputation
Mentee perspectives demonstrate that recognition creates ripple effects extending far beyond mentors themselves.
Community Recognition Visibility
Track how recognition reaches beyond immediate program:
- Media coverage analysis showing public recognition mentors receive
- Social media engagement metrics indicating recognition post reach and impact
- Community member feedback about mentor recognition awareness
- College admissions officer perspectives on how recognition documentation affects applications
- Employer feedback when mentor alumni cite recognition in hiring contexts
External visibility analysis reveals whether recognition effectively communicates program value to stakeholder audiences whose perceptions influence recruitment, funding, and institutional support.
Technology Solutions for Scalable Senior Mentor Recognition
Managing comprehensive recognition programs requires technology enabling efficient operations and meaningful engagement.
Digital Recognition Display Systems
For schools with physical facilities, interactive displays create engaging recognition experiences:
As mentioned earlier, Rocket Alumni Solutions provides platforms specifically designed for educational institutions combining intuitive content management accessible to non-technical staff, professional display hardware designed for continuous public use, engaging user interfaces encouraging extended exploration, unlimited recognition capacity accommodating all mentors without space constraints, and comprehensive analytics showing which content resonates most with viewers.
Digital recognition proves particularly valuable for mentorship programs needing to demonstrate impact to administrators, families, and community members visiting schools. The ability to instantly update content ensures recognition always reflects current mentors rather than becoming embarrassingly outdated.
Content Management and Communications Platforms
Cloud-based systems streamline recognition program operations:
Centralized Recognition Tracking
Purpose-built platforms provide comprehensive management through mentor profile databases storing biographical information, photos, and achievements, recognition award tracking documenting what acknowledgment each mentor received, milestone automation triggering recognition when mentors reach participation benchmarks, communication tools facilitating recognition announcements and invitations, and reporting capabilities demonstrating program scope and impact.
Multi-Channel Distribution
Effective platforms enable consistent recognition across formats including website integration displaying mentors on school sites, social media publishing automating recognition post creation, email distribution sending recognition announcements to families and community, digital signage updating displays throughout school buildings, and mobile access enabling recognition exploration from any device.
Multi-channel consistency ensures mentors receive comprehensive acknowledgment rather than fragmented recognition depending on which platforms viewers happen to access.
Connecting Mentor Recognition to Broader Student Success Initiatives
Maximum impact comes from integrating mentor recognition with comprehensive student support and leadership development:
Recognition as Leadership Development
Frame recognition as essential element of leadership learning:
Reflection and Growth Orientation
Use recognition moments to prompt mentor self-reflection through awards ceremonies incorporating mentor speeches about leadership learning, recognition portfolios requiring mentors to document growth and achievement, feedback loops where recognized mentors share insights benefiting future cohorts, goal-setting connections linking recognition to continued development, and mentor alumni connections showing long-term leadership trajectories.
This developmental framing ensures recognition serves educational purposes beyond simple acknowledgment, reinforcing that the process of earning recognition through service and growth matters as much as the recognition itself.
Pathway Building
Connect mentor recognition to future opportunities through college application support helping mentors articulate recognition in essays, leadership program recruitment leveraging mentor recognition for selective opportunities, scholarship connections highlighting mentor recognition-scholarship program relationships, career networking introducing recognized mentors to professionals in their fields, and continuing education resources supporting mentor alumni professional development.
Recognition becomes gateway rather than endpoint, opening doors to expanded opportunities justified by demonstrated leadership capabilities.
Institutional Culture Development
Strategic recognition shapes broader school culture:
Values Communication
Recognition demonstrates institutional priorities through visible celebration of service alongside academic and athletic achievement, leadership acknowledgment comparable to traditional honors and accolades, peer support emphasis showing schools value students helping students, and diversity celebration ensuring recognition includes mentors from all backgrounds.
The recognition schools choose to provide publicly signals what they genuinely value beyond mission statements and philosophical documents. Consistent mentor recognition demonstrates authentic commitment to leadership development and student-centered support.
Aspirational Modeling
Recognition creates achievement templates younger students can follow:
- Clear pathways showing how students can earn similar recognition
- Accessible examples demonstrating that recognition doesn’t require exceptional talent, just commitment
- Diverse representation ensuring all students see “people like me” among recognized mentors
- Progressive development showing recognition available at different skill and involvement levels
- Long-term trajectories connecting early mentor involvement to significant future achievement
This aspirational function transforms recognition from acknowledgment of past achievement into inspiration for future participation, creating sustainable pipelines of student leaders committed to serving their peers and communities. Explore student success and recognition strategies that build comprehensive development pathways.
Conclusion: Building Sustainable Mentor Recognition Programs
Senior student mentors represent tremendous yet often underutilized assets in educational communities. These peer leaders provide irreplaceable support that professional educators, despite their skill and dedication, cannot fully replicate. They bridge social gaps, transmit cultural knowledge, offer credible guidance rooted in recent shared experience, and develop sophisticated leadership capabilities through their service.
Effective recognition honors these contributions while creating systemic benefits extending throughout school communities. Recognition validates mentor commitment and sacrifice, inspires future generations of student leaders, demonstrates institutional values to families and stakeholders, documents leadership development valuable for applications and career advancement, and builds sustainable pipelines ensuring continued program vitality.
The strategies explored throughout this guide provide comprehensive frameworks for creating recognition systems that feel meaningful and authentic rather than perfunctory or generic. From multi-tiered structures ensuring continuous acknowledgment to personalized approaches celebrating individual contributions, from traditional formats providing tangible documentation to modern digital solutions enabling unlimited capacity and engaging storytelling, these approaches transform mentor recognition from occasional token gestures to systematic celebration woven throughout institutional culture.
Celebrate Your Senior Mentors and Build Leadership Culture
Discover how modern recognition solutions help schools honor student mentor contributions, inspire future leaders, and build thriving mentorship programs that strengthen entire communities.
Explore Recognition SolutionsBuilding effective senior mentor recognition requires moving beyond limiting assumptions about student service deserving only modest acknowledgment separate from “real” achievements like athletic or academic honors. When schools provide mentors with recognition equal to any other accomplishment, they communicate authentic values while inspiring broader participation in peer leadership that transforms school culture and student success outcomes.
Start where you are with recognition you can implement immediately—morning announcements, social media posts, simple certificates documenting service. Then systematically expand toward comprehensive approaches featuring permanent displays, formal ceremonies, digital recognition platforms, and integrated acknowledgment woven throughout school operations and communications.
Your senior mentors deserve celebration commensurate with the profound impact they create supporting younger peers. With thoughtful planning, appropriate technology solutions like those available through Rocket Alumni Solutions, and consistent implementation, you can build recognition systems that honor every mentor’s contributions while inspiring future generations of student leaders committed to serving their communities.
Ready to enhance your senior mentor recognition? Explore comprehensive approaches to outstanding student recognition that celebrate diverse achievements, discover honor roll recognition strategies applicable to leadership acknowledgment, learn about student stem project recognition showcasing specialized contributions, and investigate national honor society recognition approaches that can inform mentorship celebration. When you’re ready to implement professional recognition systems, connect with Rocket Alumni Solutions to explore platforms designed specifically for schools prioritizing student leadership and peer support.
Your senior mentors represent your institution’s living legacy—current students whose leadership shapes school culture while developing capabilities that will serve them throughout their lives. They deserve recognition that honors their service, celebrates their growth, and inspires continued commitment to helping others succeed. Make their contributions visible, celebrate their achievements, and create the culture where serving peers earns respect equal to any other accomplishment your school community values.